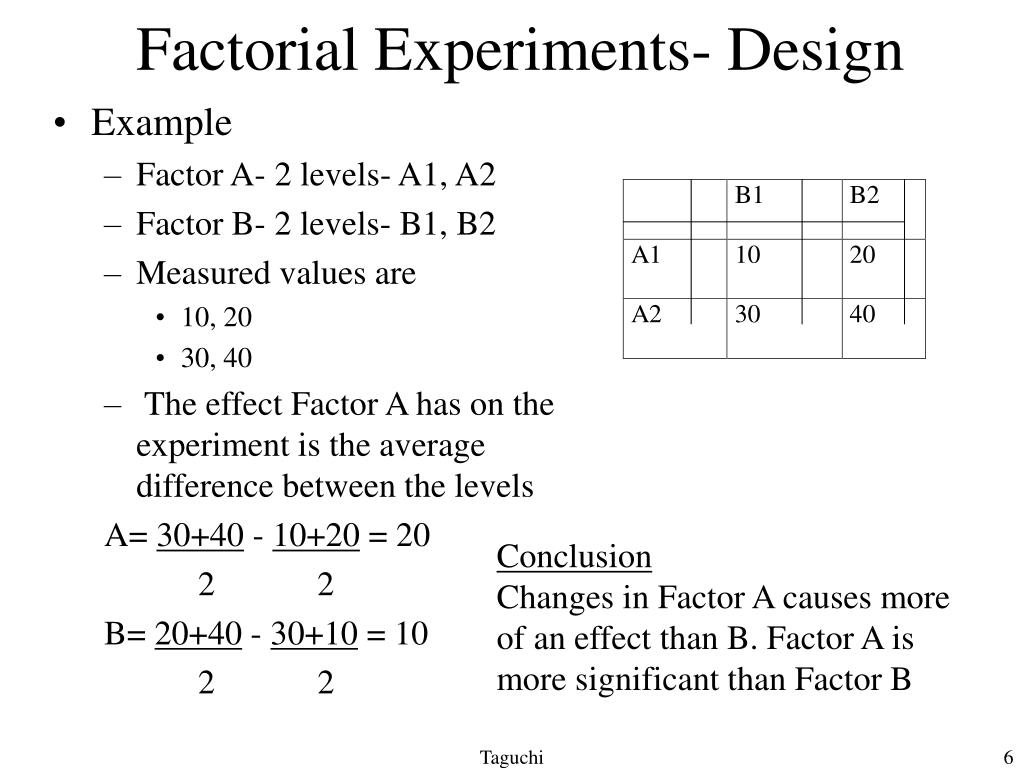
A 4 X 3 Factorial Design Would Have How Many Conditions
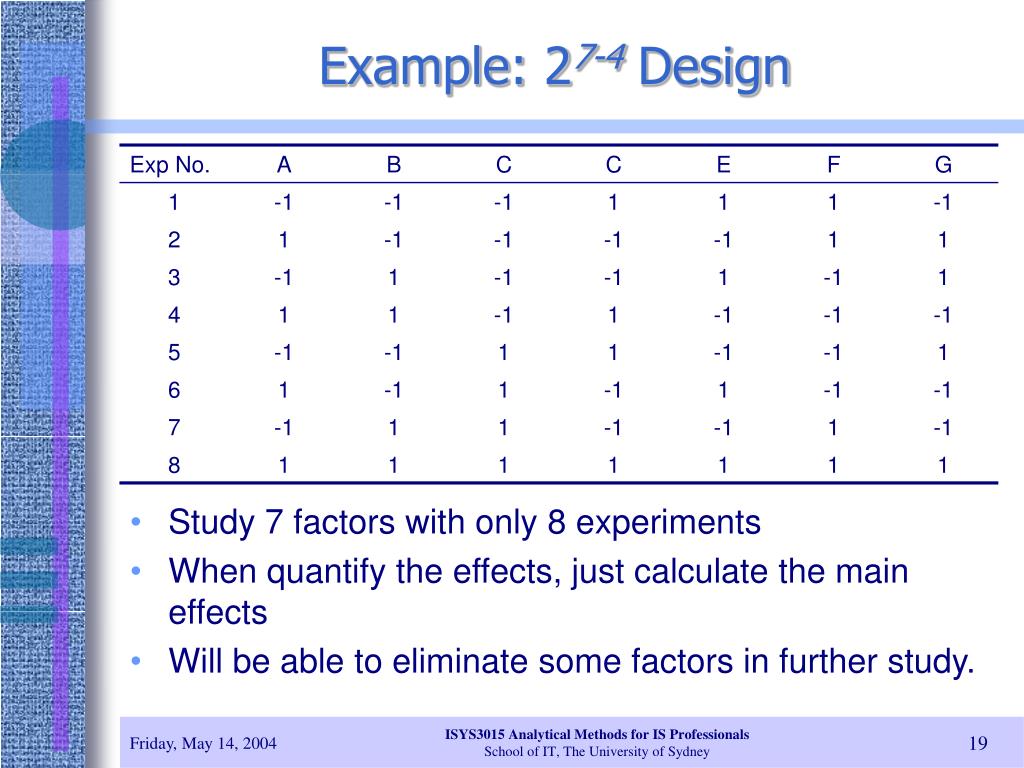
A 4 X 3 Factorial Design Would Have How Many Conditions - A factorial design table shows the number of conditions. (4 x 3 x 2) = 24 different conditions. A 2x2 factorial design has 4. In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3 levels of another factor). Each combination becomes a condition in the experiment; In a 4 × 3 factorial design with a repeated measures design, if you want 20 participants per condition, you would need 20. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a 4 × 3 factorial design would have _____ conditions., a researcher designs a. This type of design has how many different conditions that subjects can be randomly assigned to?
In a 4 × 3 factorial design with a repeated measures design, if you want 20 participants per condition, you would need 20. A 2x2 factorial design has 4. (4 x 3 x 2) = 24 different conditions. This type of design has how many different conditions that subjects can be randomly assigned to? A factorial design table shows the number of conditions. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a 4 × 3 factorial design would have _____ conditions., a researcher designs a. Each combination becomes a condition in the experiment; In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3 levels of another factor).
(4 x 3 x 2) = 24 different conditions. A 2x2 factorial design has 4. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a 4 × 3 factorial design would have _____ conditions., a researcher designs a. A factorial design table shows the number of conditions. Each combination becomes a condition in the experiment; This type of design has how many different conditions that subjects can be randomly assigned to? In a 4 × 3 factorial design with a repeated measures design, if you want 20 participants per condition, you would need 20. In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3 levels of another factor).
SOLVED The following are factorial designs (betweengroups) 1
In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3 levels of another factor). A 2x2 factorial design has 4. Each combination becomes a condition in the experiment; In a 4 × 3 factorial design with a repeated measures design, if you want 20 participants per condition, you.
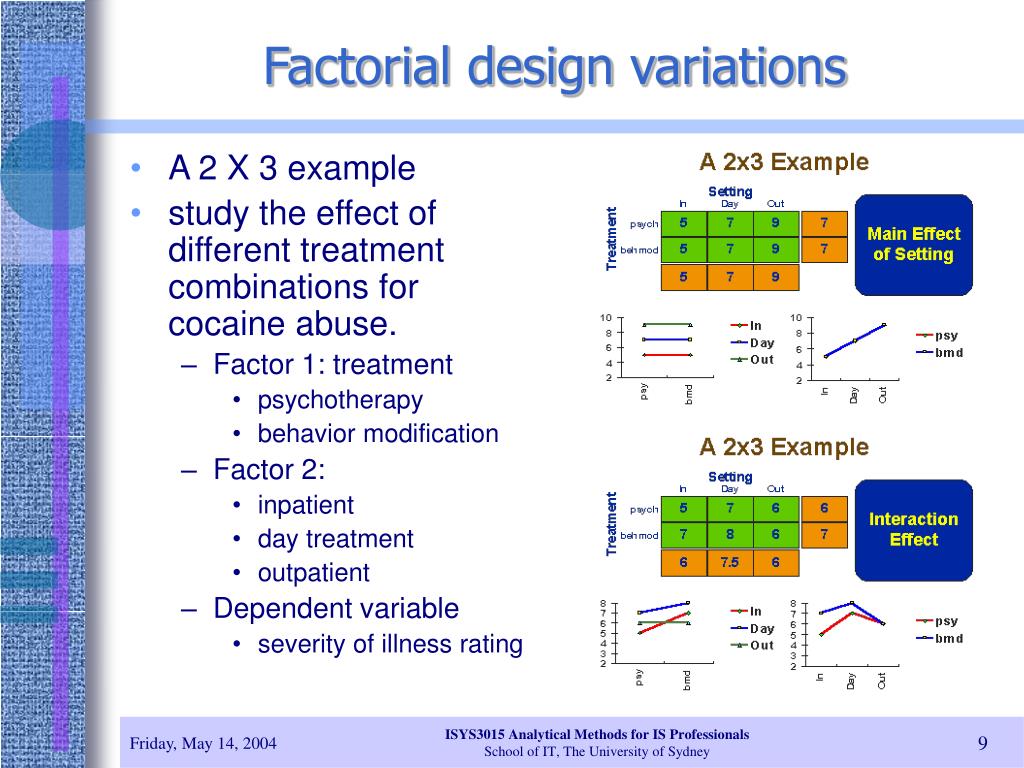
Factorial Design
A factorial design table shows the number of conditions. (4 x 3 x 2) = 24 different conditions. This type of design has how many different conditions that subjects can be randomly assigned to? In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3 levels of another factor)..
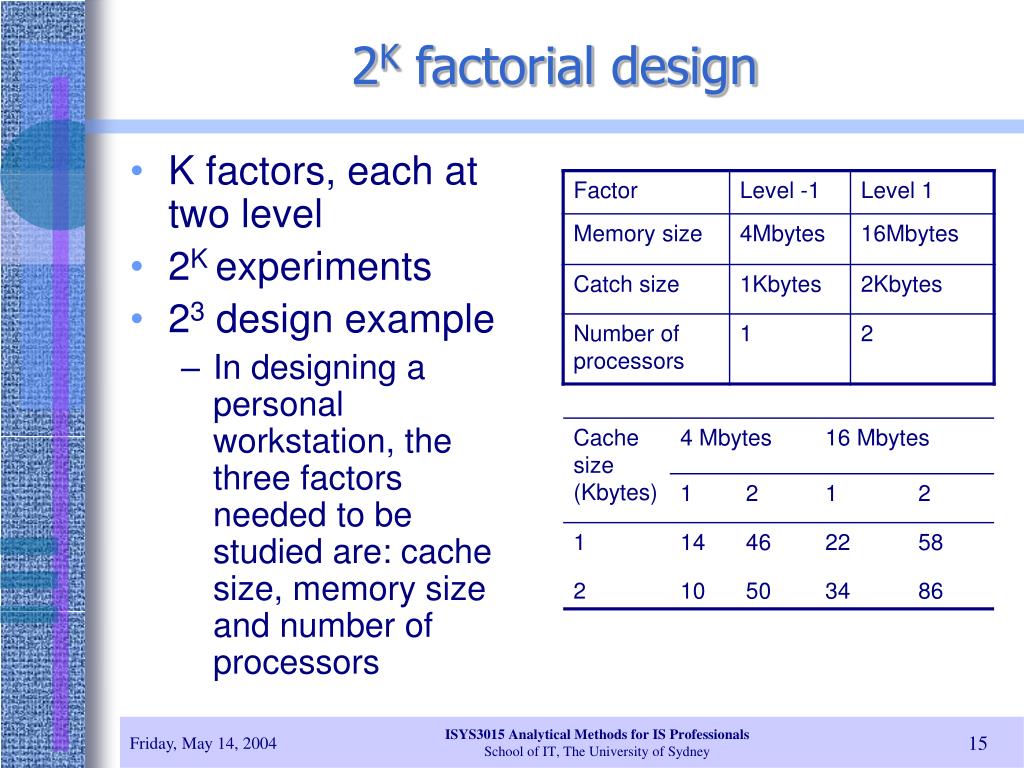
Factorial Design
In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3 levels of another factor). This type of design has how many different conditions that subjects can be randomly assigned to? (4 x 3 x 2) = 24 different conditions. A 2x2 factorial design has 4. In a 4.
Factorial Design
In a 4 × 3 factorial design with a repeated measures design, if you want 20 participants per condition, you would need 20. (4 x 3 x 2) = 24 different conditions. A 2x2 factorial design has 4. In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3.
Factorial Design
In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3 levels of another factor). This type of design has how many different conditions that subjects can be randomly assigned to? A 2x2 factorial design has 4. In a 4 × 3 factorial design with a repeated measures design,.
Factorial Design
Each combination becomes a condition in the experiment; In a 4 × 3 factorial design with a repeated measures design, if you want 20 participants per condition, you would need 20. (4 x 3 x 2) = 24 different conditions. A factorial design table shows the number of conditions. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a 4.
Factorial Design
(4 x 3 x 2) = 24 different conditions. This type of design has how many different conditions that subjects can be randomly assigned to? In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3 levels of another factor). A 2x2 factorial design has 4. Study with quizlet.
Factorial Design
In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3 levels of another factor). (4 x 3 x 2) = 24 different conditions. Each combination becomes a condition in the experiment; This type of design has how many different conditions that subjects can be randomly assigned to? In.
Factorial Design
In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3 levels of another factor). In a 4 × 3 factorial design with a repeated measures design, if you want 20 participants per condition, you would need 20. A 2x2 factorial design has 4. This type of design has.
Factorial Design
A 2x2 factorial design has 4. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a 4 × 3 factorial design would have _____ conditions., a researcher designs a. Each combination becomes a condition in the experiment; In a 4 × 3 factorial design, there are a total of 12 conditions (4 levels of one factor multiplied by 3 levels.
In A 4 × 3 Factorial Design, There Are A Total Of 12 Conditions (4 Levels Of One Factor Multiplied By 3 Levels Of Another Factor).
Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a 4 × 3 factorial design would have _____ conditions., a researcher designs a. A factorial design table shows the number of conditions. A 2x2 factorial design has 4. (4 x 3 x 2) = 24 different conditions.
This Type Of Design Has How Many Different Conditions That Subjects Can Be Randomly Assigned To?
In a 4 × 3 factorial design with a repeated measures design, if you want 20 participants per condition, you would need 20. Each combination becomes a condition in the experiment;