Cognitive Busyness
Cognitive Busyness - When audiences are cognitively busy, they are. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). Cognitive aging, busyness, cognitive engagement, episodic memory, middle age, old age. Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”.
When audiences are cognitively busy, they are. Cognitive aging, busyness, cognitive engagement, episodic memory, middle age, old age. Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount).
We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). When audiences are cognitively busy, they are. Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”. Cognitive aging, busyness, cognitive engagement, episodic memory, middle age, old age. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount).
03.2 Schlüsselstudie Gilbert Studie „On Cognitive Busyness When
We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). Cognitive aging, busyness,.
Brain activation, human mind and consciousness. Psychology, strong
Cognitive aging, busyness, cognitive engagement, episodic memory, middle age, old age. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). When audiences are cognitively busy, they are. Busyness, defined as the demands of.
7 Tips for Improving Cognitive Thinking JCU Online
We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”. Cognitive aging, busyness, cognitive engagement, episodic memory, middle age, old age. When audiences are cognitively busy, they are. We contend that.
The Influence of Cognitive Load on SelfPresentation Can Cognitive
We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). Cognitive aging, busyness, cognitive engagement, episodic memory, middle age, old age. Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”. When audiences are cognitively busy, they are. We contend that.
(PDF) The effect of cognitive busyness on consumers’ perception of
We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). When audiences are.
23 Cognitive Skills Examples (2024)
Cognitive aging, busyness, cognitive engagement, episodic memory, middle age, old age. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate.
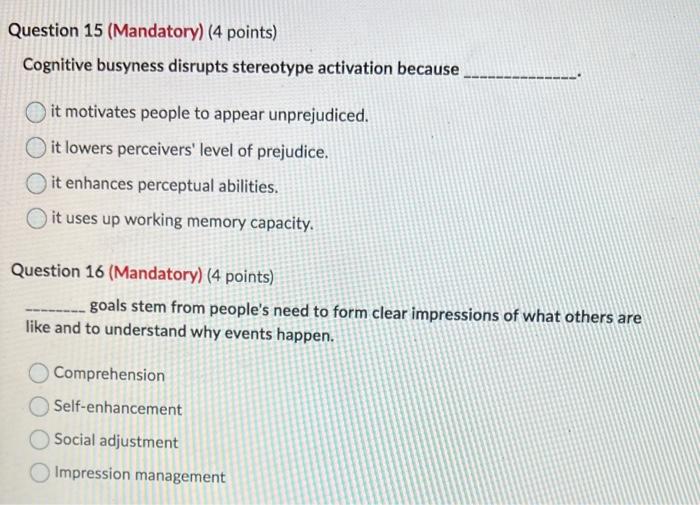
Solved Cognitive busyness disrupts stereotype activation
Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). When audiences are cognitively busy, they are. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e.,.
(PDF) Busyness, mental engagement, and stress Relationships to
We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). When audiences are cognitively busy, they are. Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e.,.
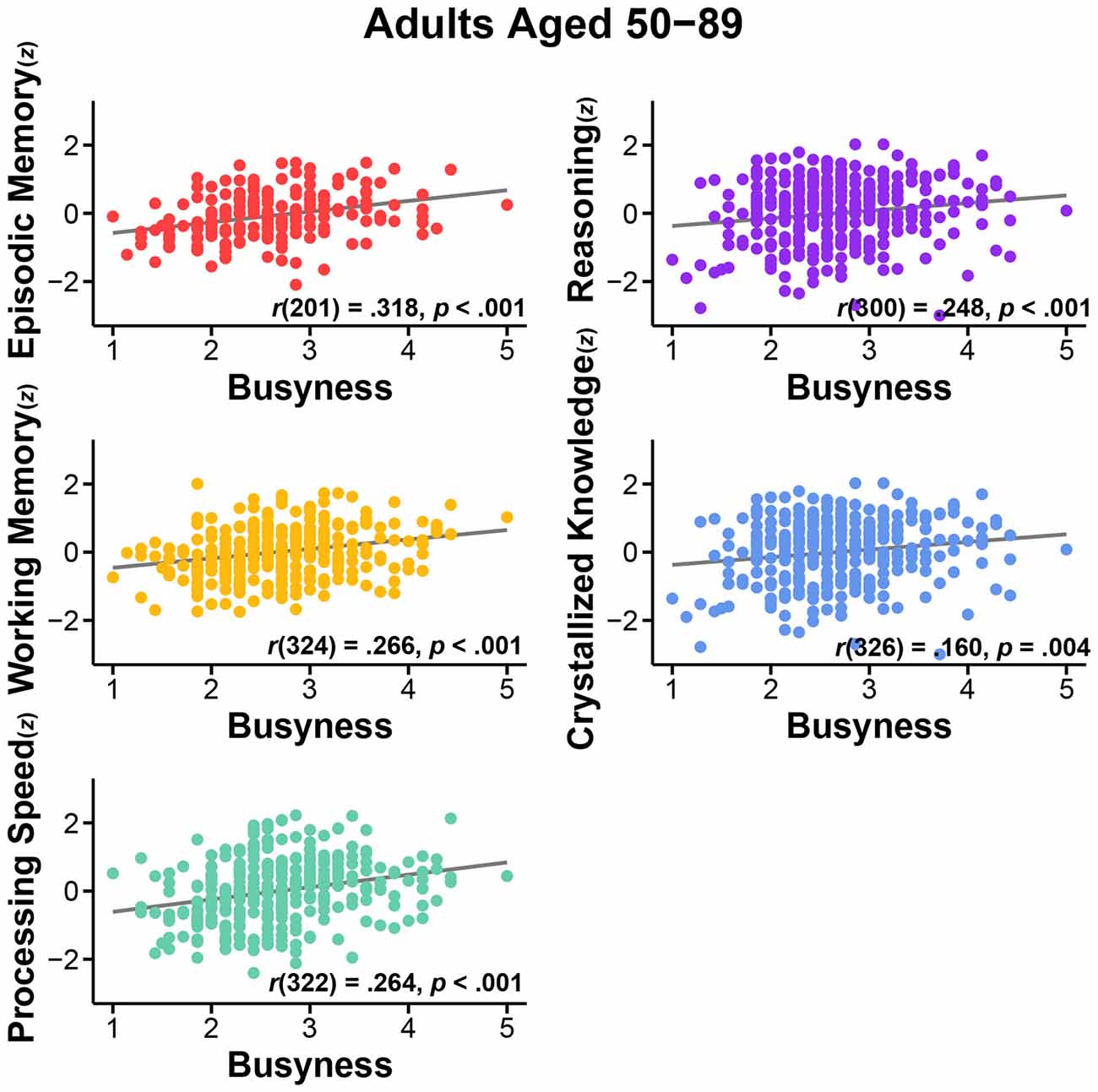
Frontiers The Busier the Better Greater Busyness Is Associated with
Cognitive aging, busyness, cognitive engagement, episodic memory, middle age, old age. When audiences are cognitively busy, they are. Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). We contend that.
Figure 1 from The Dynamics of Goal Congruency and Cognitive Busyness in
When audiences are cognitively busy, they are. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). Cognitive aging, busyness, cognitive engagement, episodic memory, middle age, old age. Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”. We contend that.
When Audiences Are Cognitively Busy, They Are.
We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). Busyness, defined as the demands of everyday life, has been shown to generate cognitive load, which has been called “cognitive busyness.”. We contend that cognitive busyness disables the ability to use situational constraint information (i.e., to augment and discount). Cognitive aging, busyness, cognitive engagement, episodic memory, middle age, old age.