Cortical Irregularity Meaning
Cortical Irregularity Meaning - Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a. It is best visualized in long bones. Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck: A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture.
Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a. Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone. A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture. It is best visualized in long bones. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck:
Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone. It is best visualized in long bones. A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck: Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a.
Physical Education and Exercise Science, Vanessa Yingling
Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone. It is best visualized in long bones. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck: Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a. A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture.
A & 3B (2020) show cortical irregularity with sclerosis involving
Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone. A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture. Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck: It is best visualized in long bones.
Plain radiographs of the left fourth digit reveal cortical irregularity
Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone. Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a. A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture. It is best visualized in long bones. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck:
Fibrous Cortical Defect Mri
The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck: It is best visualized in long bones. A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture. Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a. Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone.
Plain radiographs of the left fourth digit reveal cortical irregularity
Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone. A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture. It is best visualized in long bones. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck: Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a.
A & 3B (2020) show cortical irregularity with sclerosis involving
Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a. It is best visualized in long bones. Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone. A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck:
What is irregularity? Tradukka
It is best visualized in long bones. Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck: Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone. A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture.
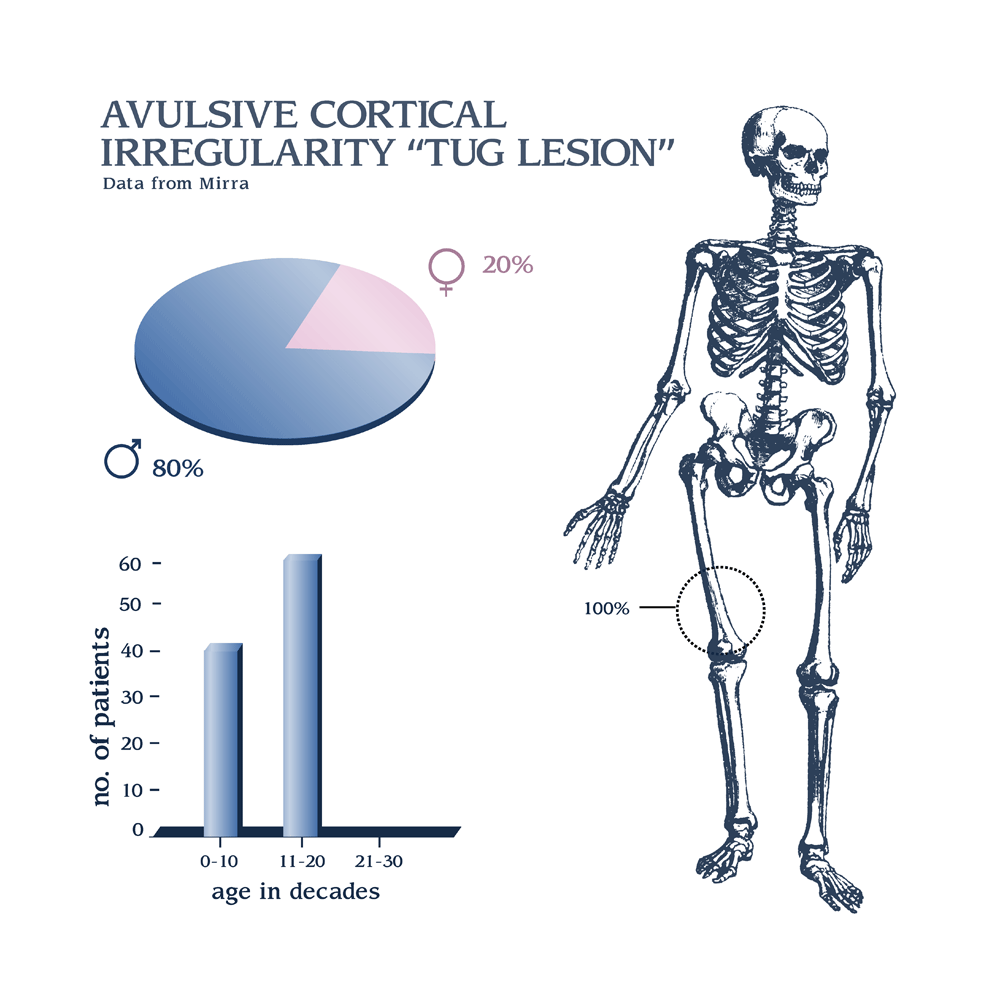
Avulsive cortical irregularity "tug lesion"
Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone. It is best visualized in long bones. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck: A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture. Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a.
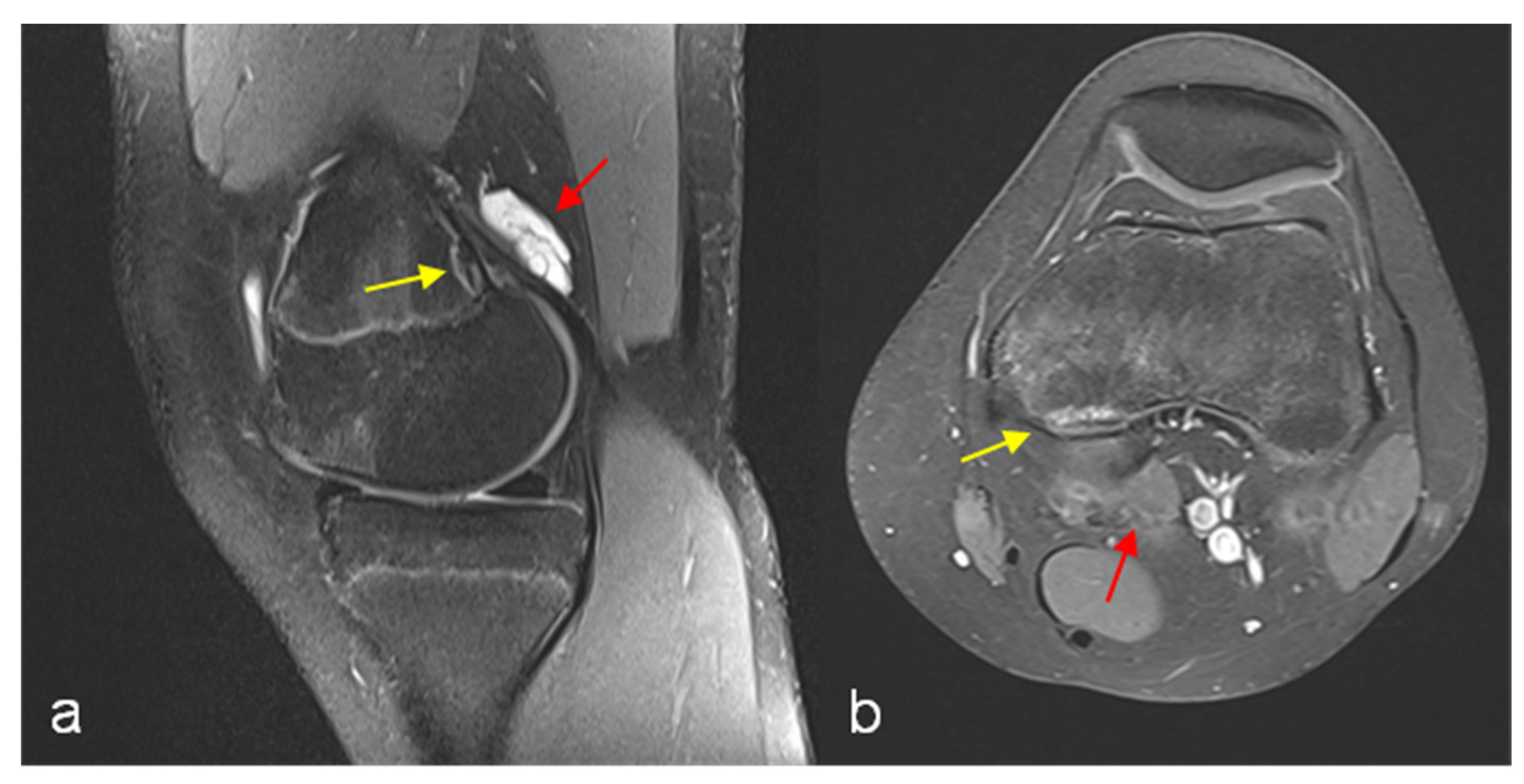
Images show examples of (ad) distal femoral cortical irregularity
A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture. Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a. It is best visualized in long bones. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck: Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone.
Bar chart shows distribution of distal femoral cortical irregularity
It is best visualized in long bones. A reliable radiographic sign of an occult radial head fracture. Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a. The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck: Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone.
A Reliable Radiographic Sign Of An Occult Radial Head Fracture.
The cortical irregularity in the transition zone of the radial head and neck: Cortical desmoids, also known as cortical avulsive injuries, bufkin lesion or distal femoral cortical defects/irregularities, are a. Cortical bone appears radiopaque (white) on radiographs as the outermost layer of bone. It is best visualized in long bones.