Forms The Bulk Of The Heavily Pigmented Vascular Layer
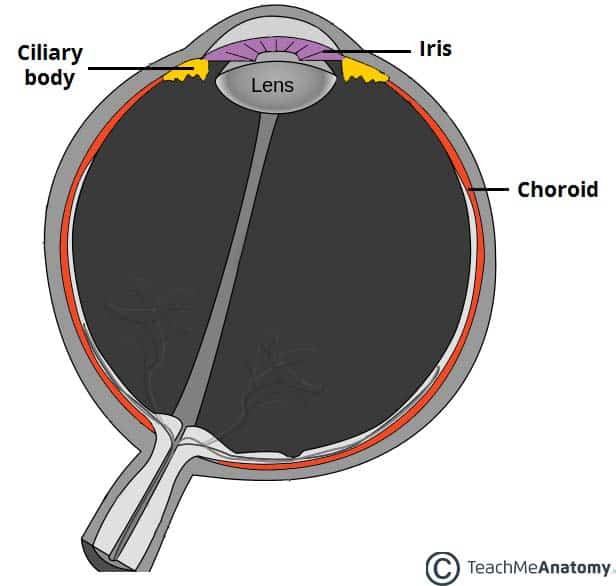
Forms The Bulk Of The Heavily Pigmented Vascular Layer - This layer provides a blood supply to the eyeball. The bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer of the eye is formed by the choroid. Forms the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer: Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like aqueous humor, sclera, optic disc and more. The choroid, a heavily pigmented vascular layer, forms the largest part of the eye. In the neural layer, the neuron populations are arranged as follows. It delivers oxygen and nutrients to the outer layers. The two major layers of the retina are the pigmented and neural layers. This layer is richly supplied with blood vessels and. The choroid plexuses form the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer in the eye.
This layer is richly supplied with blood vessels and. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like aqueous humor, sclera, optic disc and more. Forms the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer: In the neural layer, the neuron populations are arranged as follows. The two major layers of the retina are the pigmented and neural layers. The choroid plexuses form the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer in the eye. It delivers oxygen and nutrients to the outer layers. The choroid, a heavily pigmented vascular layer, forms the largest part of the eye. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like fluid. The bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer of the eye is formed by the choroid.
In the neural layer, the neuron populations are arranged as follows. This layer is richly supplied with blood vessels and. The choroid, a heavily pigmented vascular layer, forms the largest part of the eye. Forms the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer: This layer provides a blood supply to the eyeball. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like fluid. Composed of tough, white, opaque, fibrous connective tissue. It delivers oxygen and nutrients to the outer layers. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like aqueous humor, sclera, optic disc and more. The two major layers of the retina are the pigmented and neural layers.
20.1 Structure and Function of Blood Vessels Douglas College Human
The bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer of the eye is formed by the choroid. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like aqueous humor, sclera, optic disc and more. This layer is richly supplied with blood vessels and. Forms the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer: Composed of tough, white, opaque, fibrous connective tissue.
Pigmentation Biology for Majors II
It delivers oxygen and nutrients to the outer layers. The two major layers of the retina are the pigmented and neural layers. Composed of tough, white, opaque, fibrous connective tissue. The choroid, a heavily pigmented vascular layer, forms the largest part of the eye. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like fluid.
Vascular tunic neurolader
The choroid, a heavily pigmented vascular layer, forms the largest part of the eye. This layer provides a blood supply to the eyeball. The bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer of the eye is formed by the choroid. The two major layers of the retina are the pigmented and neural layers. In the neural layer, the neuron populations are.
Sensory systems online presentation
This layer provides a blood supply to the eyeball. Forms the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer: The bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer of the eye is formed by the choroid. Composed of tough, white, opaque, fibrous connective tissue. It delivers oxygen and nutrients to the outer layers.
Retina 4 Digital Histology
It delivers oxygen and nutrients to the outer layers. This layer is richly supplied with blood vessels and. The bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer of the eye is formed by the choroid. The two major layers of the retina are the pigmented and neural layers. The choroid plexuses form the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer in.
Vision Interactive pgs ppt download
Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like fluid. In the neural layer, the neuron populations are arranged as follows. The choroid, a heavily pigmented vascular layer, forms the largest part of the eye. This layer provides a blood supply to the eyeball. The bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer of the eye is formed by the choroid.
Sensory Organs Clinical Tree
The choroid, a heavily pigmented vascular layer, forms the largest part of the eye. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like aqueous humor, sclera, optic disc and more. In the neural layer, the neuron populations are arranged as follows. The choroid plexuses form the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer in the eye. Composed of tough, white,.
Xylem Wikipedia in 2020 Tissue types, Tissue biology, Biology notes
The bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer of the eye is formed by the choroid. Forms the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer: The choroid plexuses form the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer in the eye. The choroid, a heavily pigmented vascular layer, forms the largest part of the eye. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards.
There are three layers, or tunics, of the eyeball. The fibrous layer is
In the neural layer, the neuron populations are arranged as follows. It delivers oxygen and nutrients to the outer layers. Forms the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer: Composed of tough, white, opaque, fibrous connective tissue. The choroid, a heavily pigmented vascular layer, forms the largest part of the eye.
Vascular Pigmented Layer PDF Human Eye Cornea
In the neural layer, the neuron populations are arranged as follows. This layer provides a blood supply to the eyeball. The choroid, a heavily pigmented vascular layer, forms the largest part of the eye. This layer is richly supplied with blood vessels and. The choroid plexuses form the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer in the eye.
The Two Major Layers Of The Retina Are The Pigmented And Neural Layers.
Forms the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer: Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like fluid. The choroid plexuses form the bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer in the eye. The bulk of the heavily pigmented vascular layer of the eye is formed by the choroid.
It Delivers Oxygen And Nutrients To The Outer Layers.
In the neural layer, the neuron populations are arranged as follows. This layer is richly supplied with blood vessels and. The choroid, a heavily pigmented vascular layer, forms the largest part of the eye. This layer provides a blood supply to the eyeball.
Composed Of Tough, White, Opaque, Fibrous Connective Tissue.
Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like aqueous humor, sclera, optic disc and more.




+Tunic.jpg)



