Low Lung Volumes With Bronchovascular Crowding Meaning
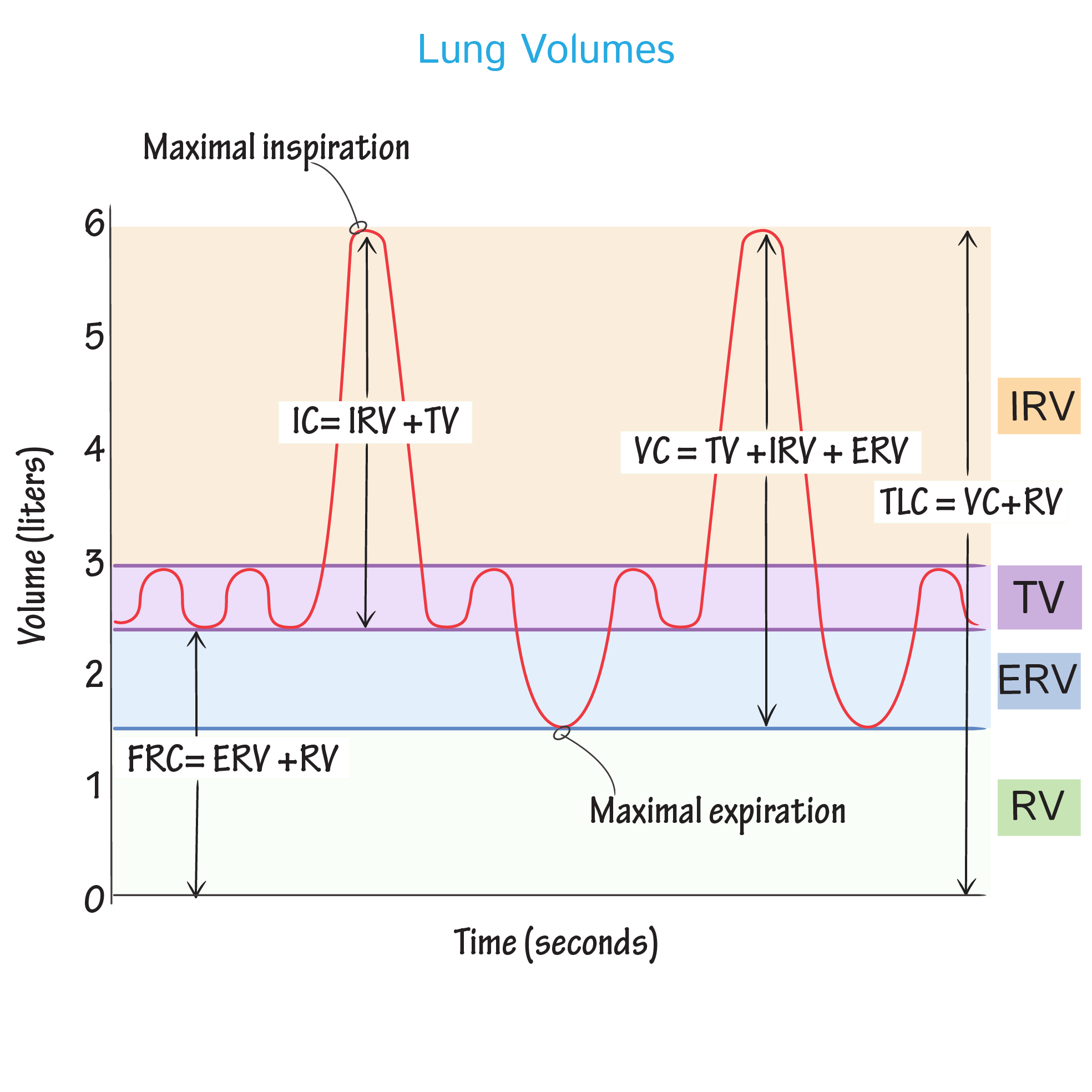
Low Lung Volumes With Bronchovascular Crowding Meaning - When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy. Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement. Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures.
Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures. When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy. Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement.
When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy. Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement. Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures.
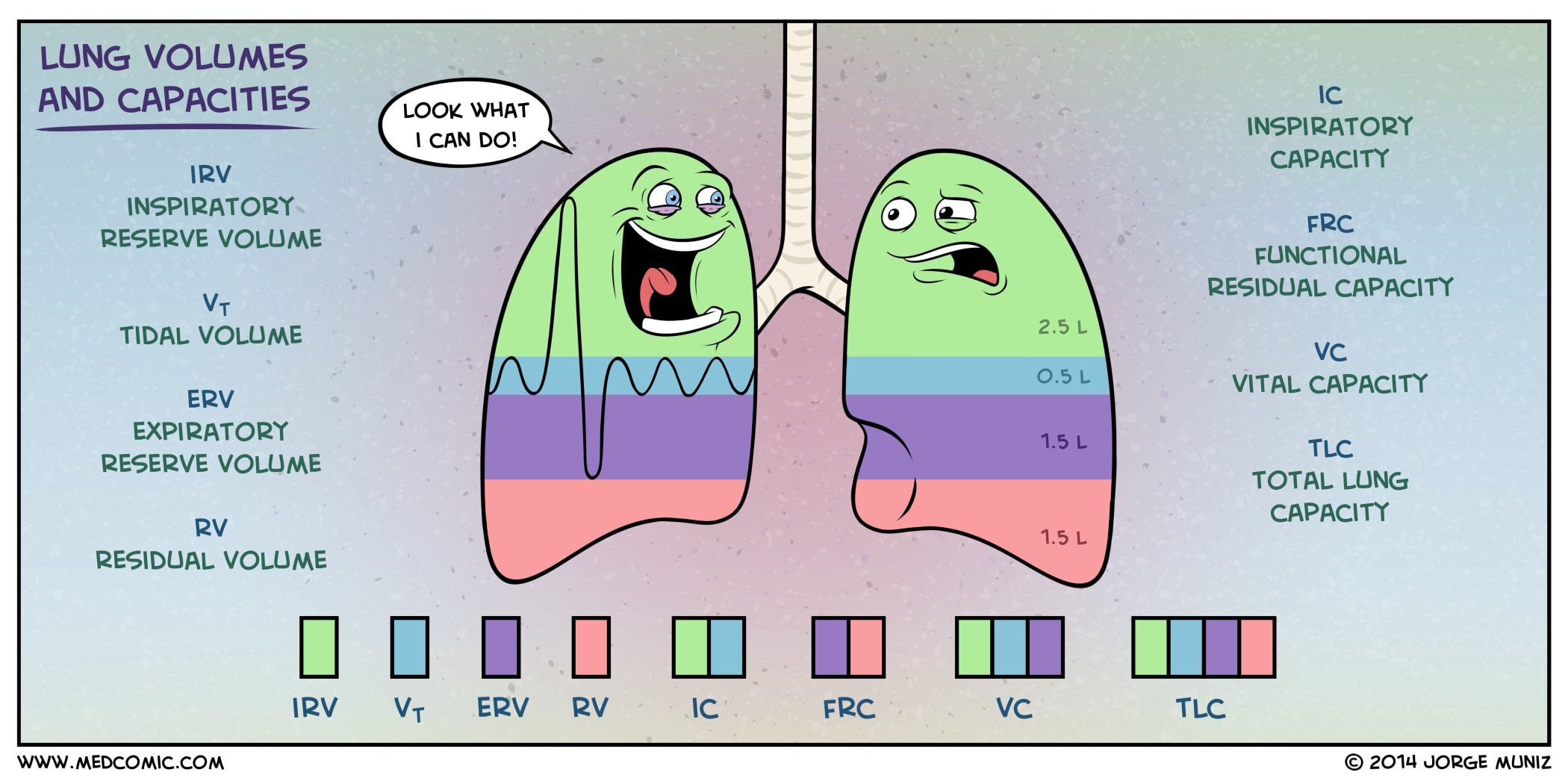
SOLUTION Lung volumes and capacities Studypool
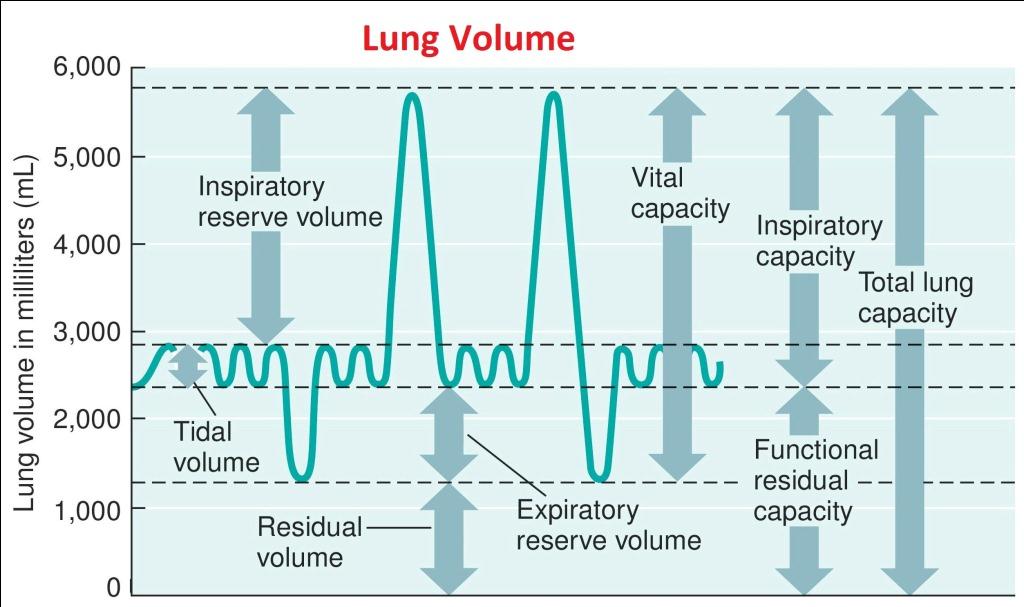
Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures. Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement. When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy.
Physiology Glossary Lung Volumes & Capacities Draw It to Know It
Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures. Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement. When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy.
Lung Volumes and Capacities
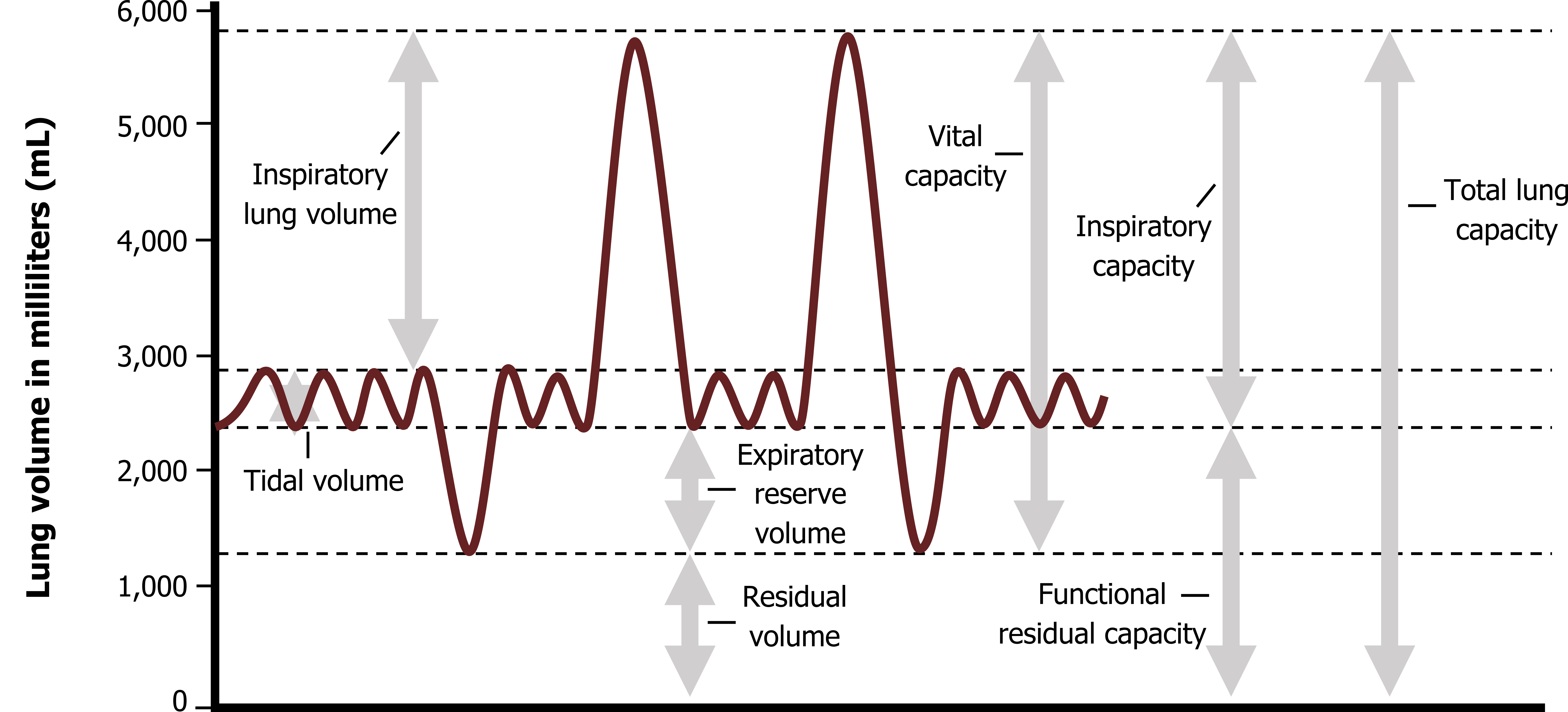
When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy. Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures. Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement.
Lung Volumes And Capacities Chart Minga
When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy. Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement. Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures.
Fig. 1. Chest radiograph reveals low lung volumes and basilar
Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures. When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy. Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement.
Xray demonstrating decreased lung volumes with central bronchovascular
Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures. Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement. When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy.
Xray demonstrating decreased lung volumes with central bronchovascular
Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement. Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures. When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy.
Lung Volumes and Capacities
Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures. Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement. When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy.
Lung Volumes and Compliance Pulmonary Physiology for PreClinical
Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement. Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures. When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy.
Portable chest radiograph showing low lung volumes and right
When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy. Other features that suggest atelectasis because of loss of volume in the involved lung include crowding of pulmonary vessels, displacement. Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures.
Other Features That Suggest Atelectasis Because Of Loss Of Volume In The Involved Lung Include Crowding Of Pulmonary Vessels, Displacement.
Direct signs of lung volume loss include fissural displacement and crowding of the bronchovascular structures. When lung volumes are low, basilar opacities resulting from atelectasis and “vascular crowding” are often evident and limit diagnostic accuracy.