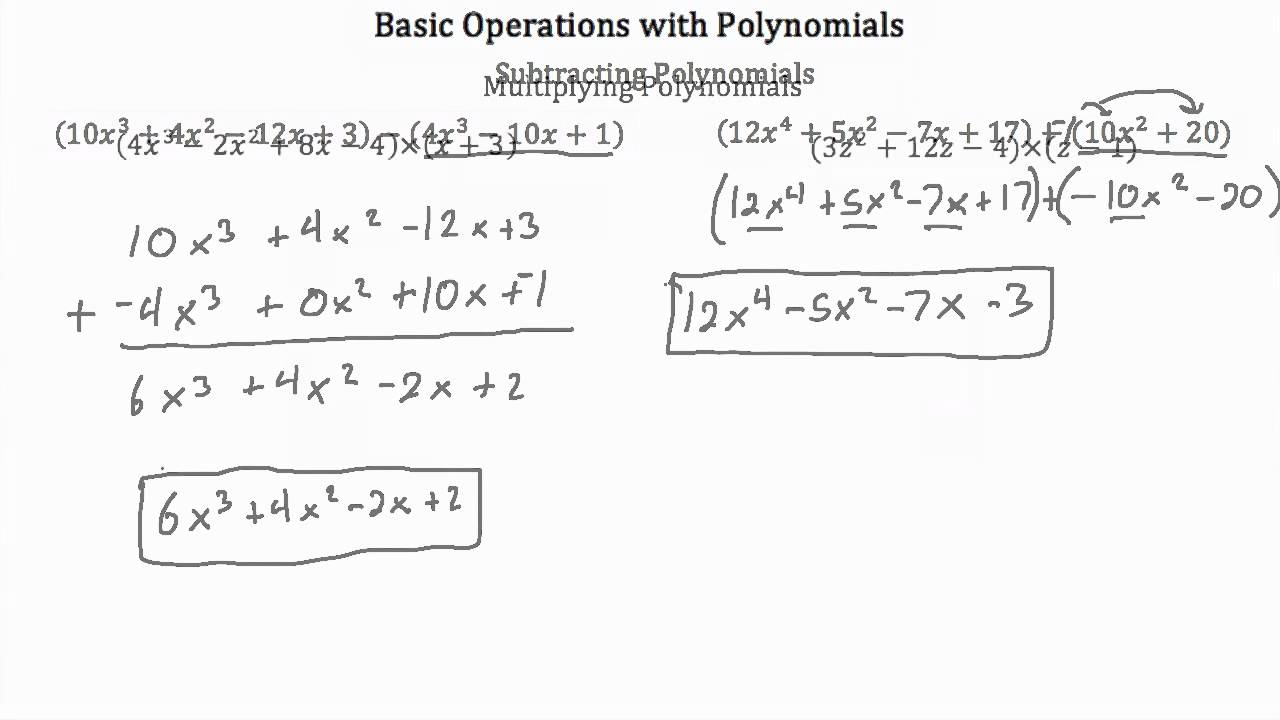
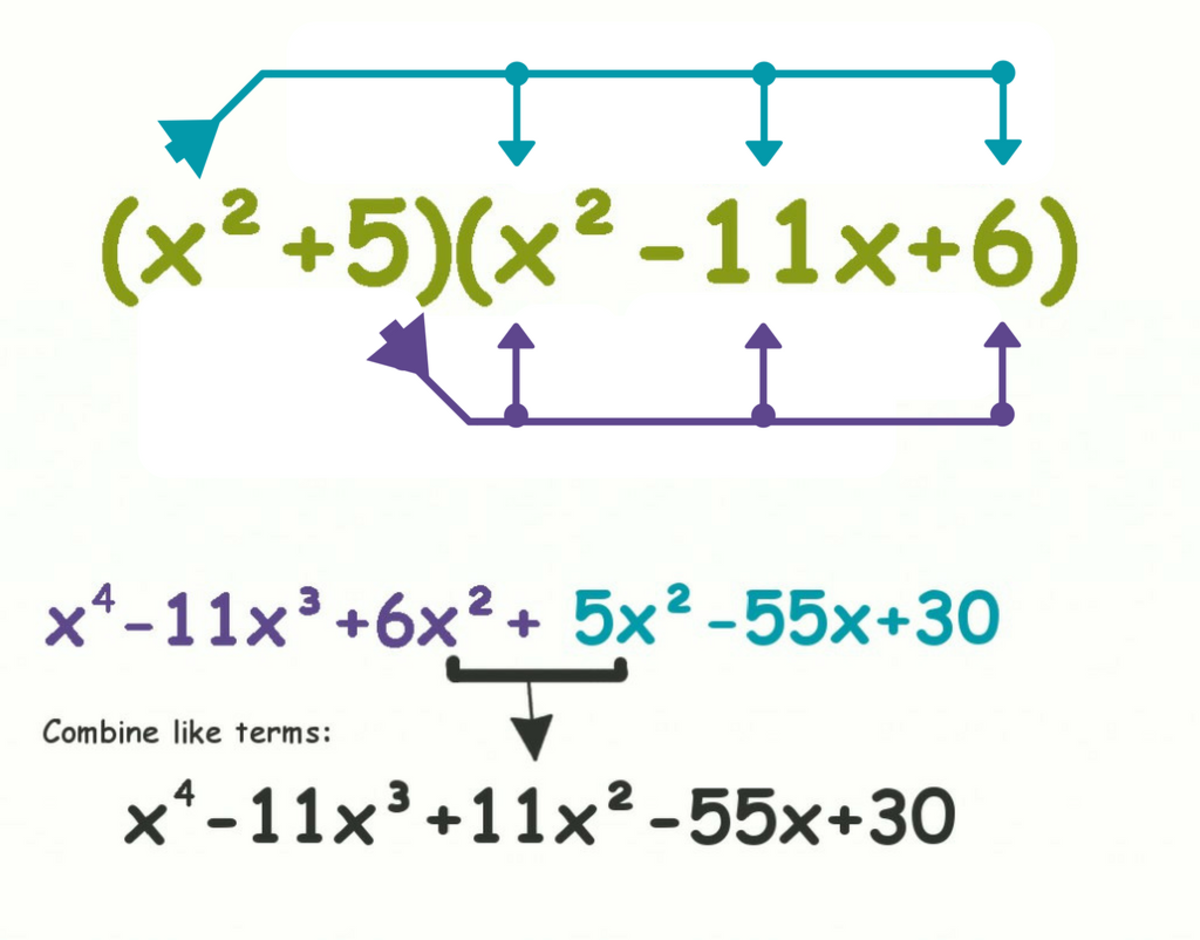
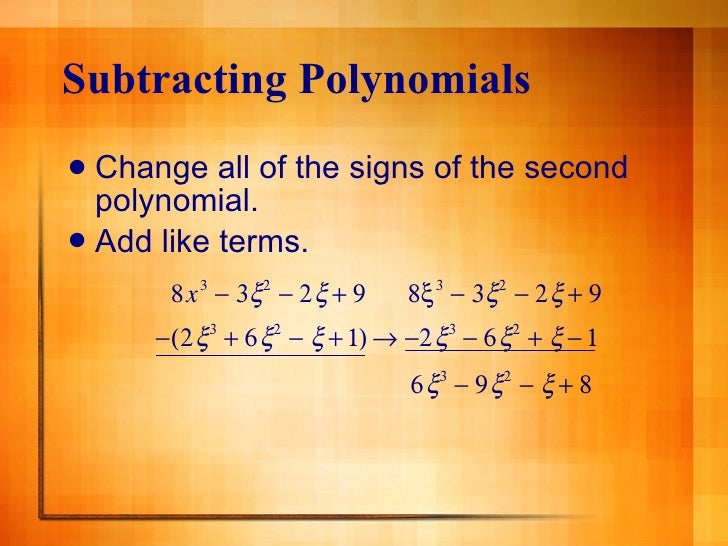
Polynomials Are Closed Under What Operations
Polynomials Are Closed Under What Operations - Under which operations are polynomials closed? The sum of two polynomials is always another. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely. Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition: Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division.
Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition: The sum of two polynomials is always another. Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely. Under which operations are polynomials closed?
The sum of two polynomials is always another. Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition: Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely. Under which operations are polynomials closed?
Solved 2. Choose the best answer. The set of polynomials is_ closed
Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition: Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely. Under which operations are polynomials closed? The sum of two polynomials is always another. Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division.
Basic Operations with Polynomials Worksheet TpT
Under which operations are polynomials closed? Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division. Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition: The sum of two polynomials is always another. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely.
Operations With Polynomials Pdf
Under which operations are polynomials closed? Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition: The sum of two polynomials is always another. Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely.
Multiply Polynomials (With Examples) FOIL Grid Methods, 52 OFF
Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition: Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely. Under which operations are polynomials closed? The sum of two polynomials is always another.
Solved Which operations are polynomials closed under? Put each type of
The sum of two polynomials is always another. Under which operations are polynomials closed? Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition: Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely.
Solved Which of these operations is not closed for polynomials? A
The sum of two polynomials is always another. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely. Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division. Under which operations are polynomials closed? Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition:
Sponsors Choose ba.operations.on.polynomials.examples/1
Under which operations are polynomials closed? Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely. Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division. Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition: The sum of two polynomials is always another.
Polynomials What are Polynomials? Definition and Examples
Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition: The sum of two polynomials is always another. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely. Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division. Under which operations are polynomials closed?
Solved Which operations are polynomials closed under? Put each type of
The sum of two polynomials is always another. Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely. Under which operations are polynomials closed? Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition:
Recursive Integration over Piecewise Polynomials Closed form
Identify the operations that are closed under polynomials * polynomial addition: The sum of two polynomials is always another. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely. Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division. Under which operations are polynomials closed?
Identify The Operations That Are Closed Under Polynomials * Polynomial Addition:
Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to integers, namely. Under which operations are polynomials closed? The sum of two polynomials is always another. Polynomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponentiation, but not under division.