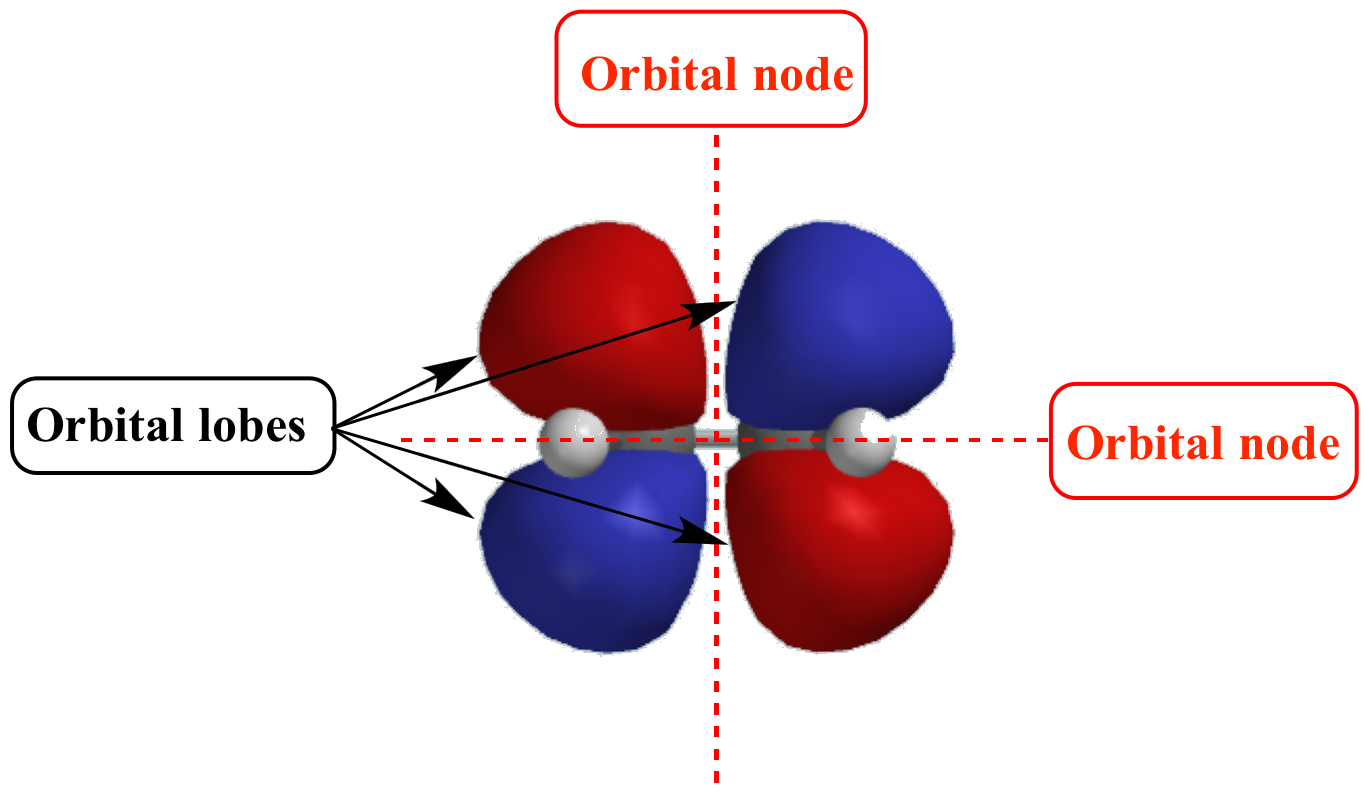
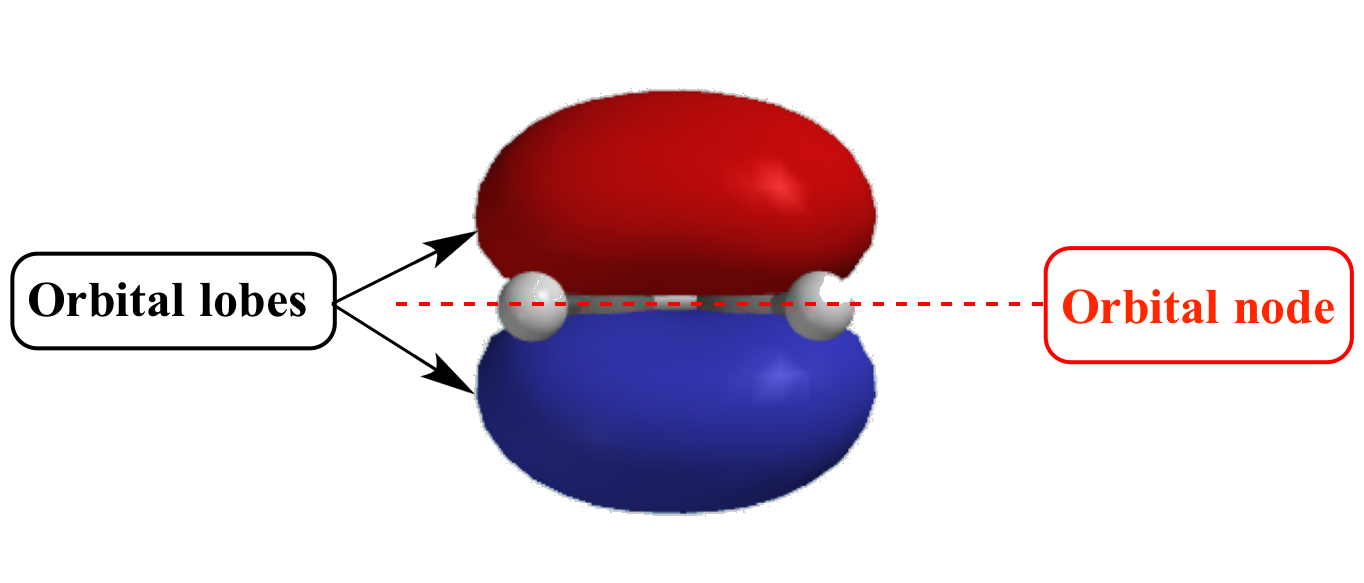
What Are Nodes In Chemistry
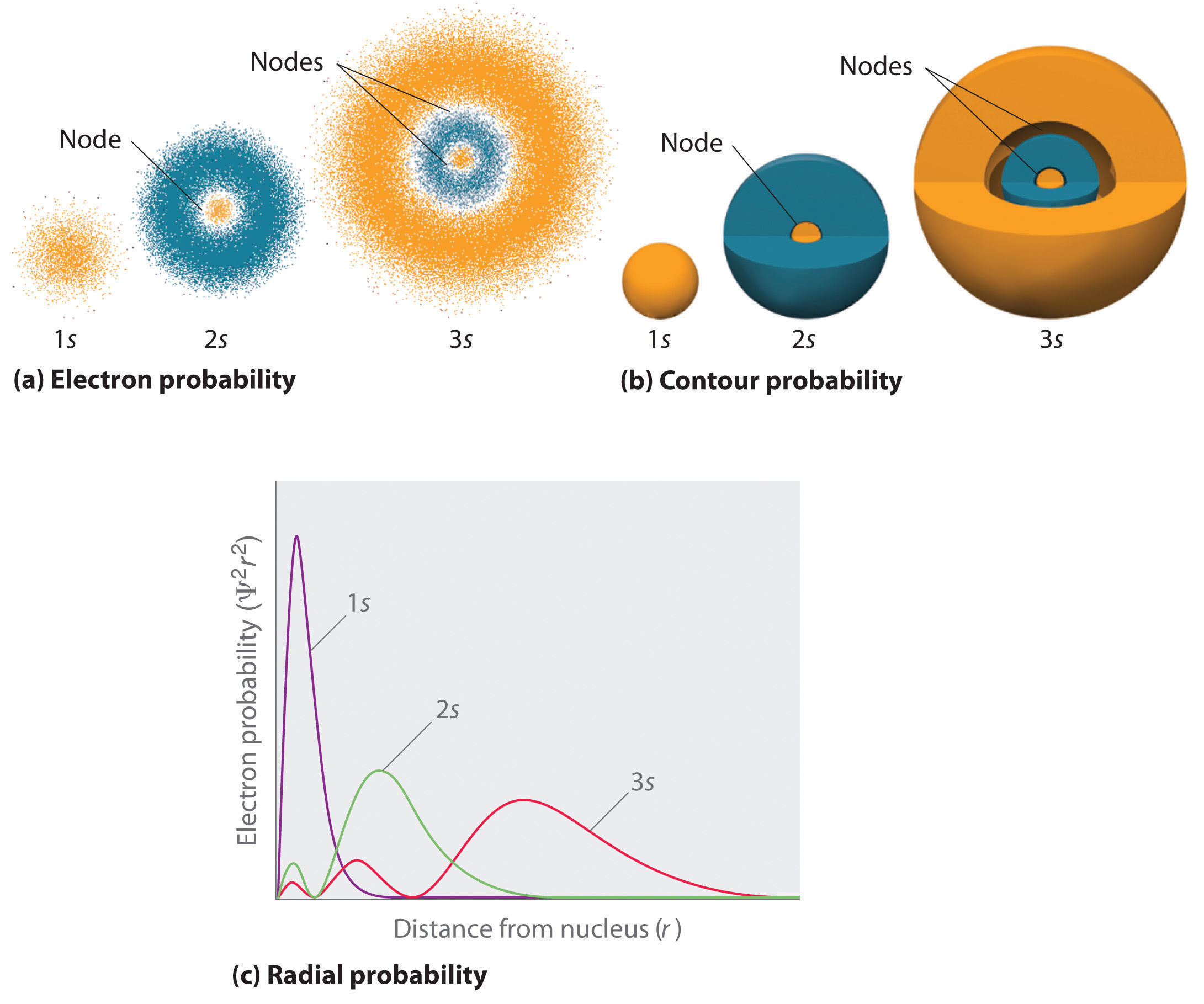
What Are Nodes In Chemistry - These spherical nodes, which separate electron shells, are known as radial nodes. Radial nodes are spherical surfaces. Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero. The number of radial nodes depends on. There are two types of nodes, angular node and radial. Learn the definitions, formulas, calculations and examples of radial and angular nodes in chemistry. In the context of atomic structure and orbitals, a node represents a specific point in space where the probability density of an electron is zero.
The number of radial nodes depends on. In the context of atomic structure and orbitals, a node represents a specific point in space where the probability density of an electron is zero. Radial nodes are spherical surfaces. Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero. Learn the definitions, formulas, calculations and examples of radial and angular nodes in chemistry. There are two types of nodes, angular node and radial. These spherical nodes, which separate electron shells, are known as radial nodes.
These spherical nodes, which separate electron shells, are known as radial nodes. Radial nodes are spherical surfaces. Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero. The number of radial nodes depends on. There are two types of nodes, angular node and radial. In the context of atomic structure and orbitals, a node represents a specific point in space where the probability density of an electron is zero. Learn the definitions, formulas, calculations and examples of radial and angular nodes in chemistry.
s Atomic Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts
In the context of atomic structure and orbitals, a node represents a specific point in space where the probability density of an electron is zero. The number of radial nodes depends on. Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero. There are two types of nodes, angular node and radial. Learn the.
Figure 1.10 from A. What Is Organic Chemistry? B. Emergence of Organic
In the context of atomic structure and orbitals, a node represents a specific point in space where the probability density of an electron is zero. The number of radial nodes depends on. Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero. Radial nodes are spherical surfaces. There are two types of nodes, angular.
Development of Quantum Theory Chemistry I
Learn the definitions, formulas, calculations and examples of radial and angular nodes in chemistry. Radial nodes are spherical surfaces. There are two types of nodes, angular node and radial. Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero. These spherical nodes, which separate electron shells, are known as radial nodes.
Question d50d3 Socratic
Learn the definitions, formulas, calculations and examples of radial and angular nodes in chemistry. The number of radial nodes depends on. Radial nodes are spherical surfaces. In the context of atomic structure and orbitals, a node represents a specific point in space where the probability density of an electron is zero. Node is referred to as a point, where the.
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Orbital node
The number of radial nodes depends on. Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero. These spherical nodes, which separate electron shells, are known as radial nodes. Learn the definitions, formulas, calculations and examples of radial and angular nodes in chemistry. Radial nodes are spherical surfaces.
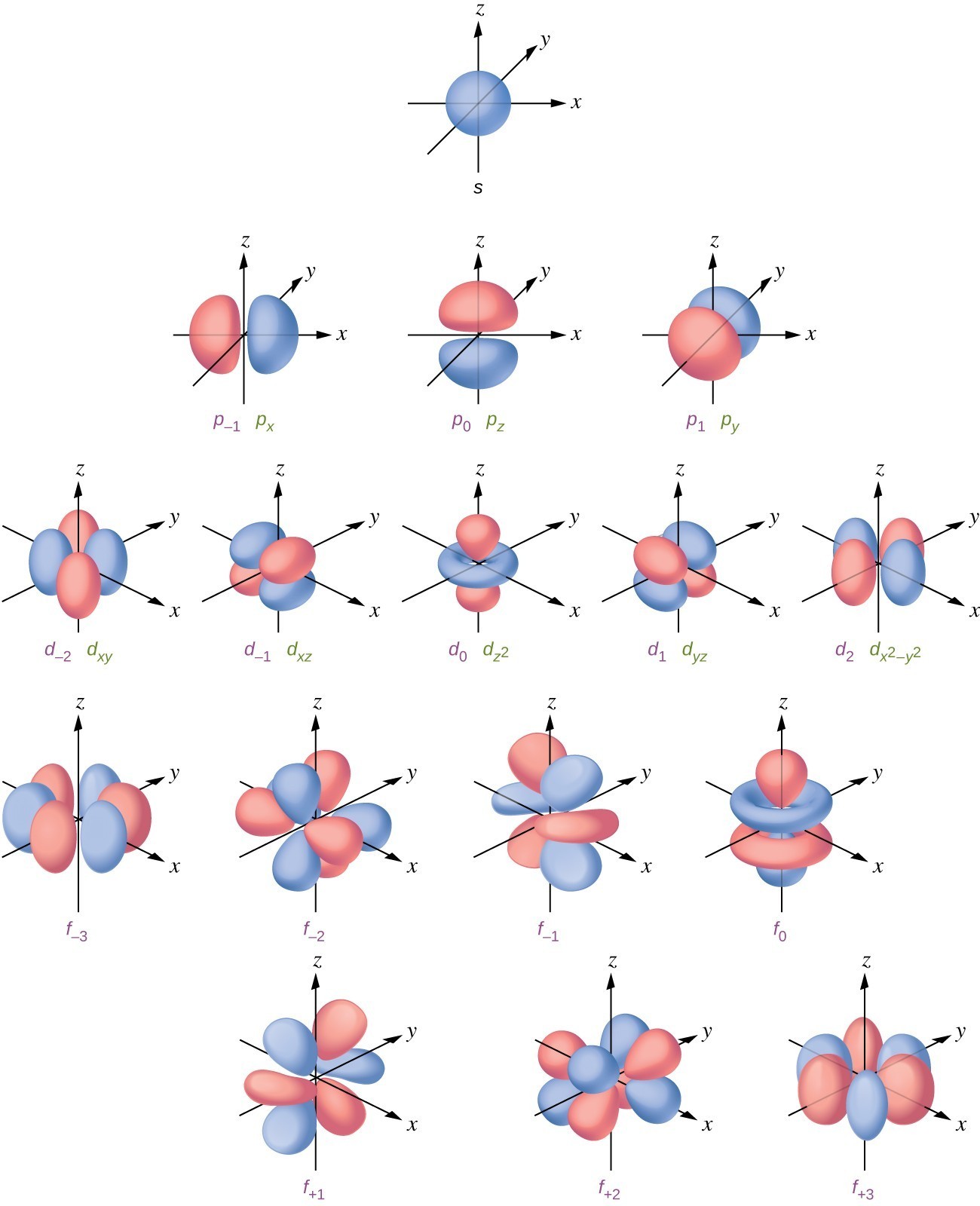
Shapes of atomic orbital Chemistry, Class 11, Structure Of Atom
Radial nodes are spherical surfaces. There are two types of nodes, angular node and radial. In the context of atomic structure and orbitals, a node represents a specific point in space where the probability density of an electron is zero. The number of radial nodes depends on. These spherical nodes, which separate electron shells, are known as radial nodes.
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Orbital node
Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero. There are two types of nodes, angular node and radial. These spherical nodes, which separate electron shells, are known as radial nodes. The number of radial nodes depends on. In the context of atomic structure and orbitals, a node represents a specific point in.
Higher Secondary Chemistry Chapter 2.16 Radial Nodes and Angular Nodes
Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero. In the context of atomic structure and orbitals, a node represents a specific point in space where the probability density of an electron is zero. The number of radial nodes depends on. Radial nodes are spherical surfaces. Learn the definitions, formulas, calculations and examples.
Doodles in the Membrane Free Educational Resources for STEM Students
These spherical nodes, which separate electron shells, are known as radial nodes. Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero. The number of radial nodes depends on. There are two types of nodes, angular node and radial. Radial nodes are spherical surfaces.
Radial and Angular nodes formula Definitions, Formula, Calculations
Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero. Radial nodes are spherical surfaces. In the context of atomic structure and orbitals, a node represents a specific point in space where the probability density of an electron is zero. There are two types of nodes, angular node and radial. Learn the definitions, formulas,.
In The Context Of Atomic Structure And Orbitals, A Node Represents A Specific Point In Space Where The Probability Density Of An Electron Is Zero.
Learn the definitions, formulas, calculations and examples of radial and angular nodes in chemistry. There are two types of nodes, angular node and radial. Radial nodes are spherical surfaces. The number of radial nodes depends on.
These Spherical Nodes, Which Separate Electron Shells, Are Known As Radial Nodes.
Node is referred to as a point, where the probability of finding the electron is zero.

.png)