What Is Acceleration Due To Gravity On The Moon
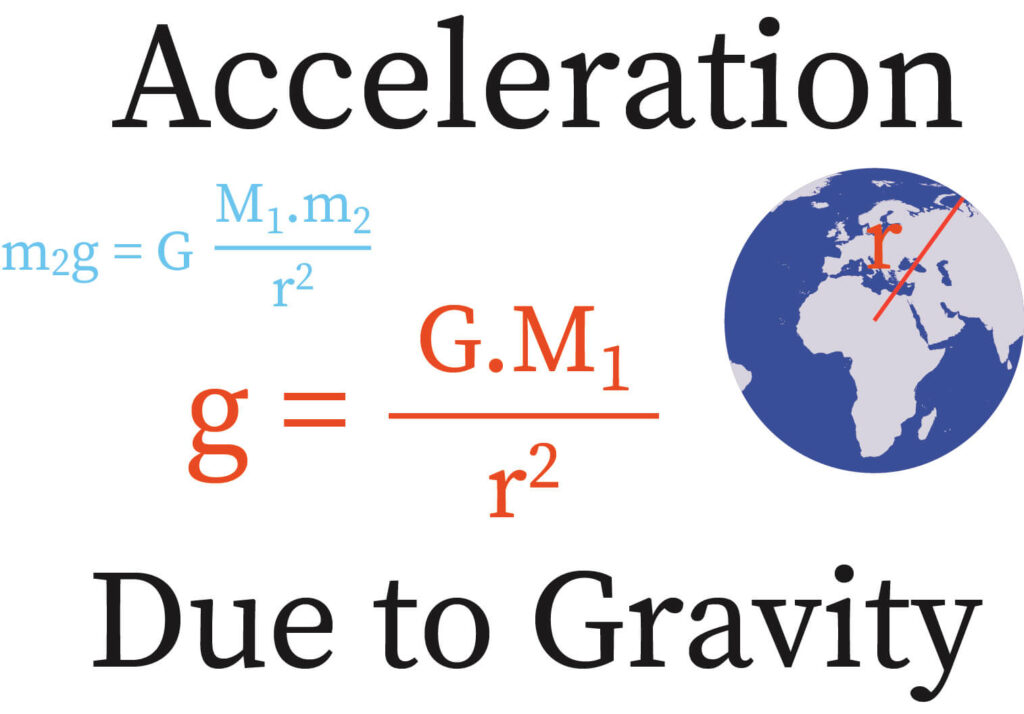
What Is Acceleration Due To Gravity On The Moon - The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is approximately 1.625 m/s 2, about 16.6% that on earth's surface or 0.166 ɡ. It is equal to 1.625 m/s 2. G = gm/r² and is about 3.71 m/s². Its unit of measurement is m/s 2. On mars, it can be calculated using the formula: The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.62 m/s^2, while on earth, it’s around 9.81 m/s^2. The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body is known as acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol 'g'. [1] over the entire surface, the variation in gravitational. This means that on the moon, you can jump higher, throw farther, and carry heavier. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.6 m/s².
The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body is known as acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol 'g'. G = gm/r² and is about 3.71 m/s². The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.6 m/s². The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is approximately 1.625 m/s 2, about 16.6% that on earth's surface or 0.166 ɡ. On mars, it can be calculated using the formula: This means that on the moon, you can jump higher, throw farther, and carry heavier. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.62 m/s^2, while on earth, it’s around 9.81 m/s^2. It is equal to 1.625 m/s 2. [1] over the entire surface, the variation in gravitational. Its unit of measurement is m/s 2.
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is approximately 1.625 m/s 2, about 16.6% that on earth's surface or 0.166 ɡ. This means that on the moon, you can jump higher, throw farther, and carry heavier. It is equal to 1.625 m/s 2. The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body is known as acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol 'g'. G = gm/r² and is about 3.71 m/s². The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.6 m/s². Its unit of measurement is m/s 2. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.62 m/s^2, while on earth, it’s around 9.81 m/s^2. [1] over the entire surface, the variation in gravitational. On mars, it can be calculated using the formula:
Acceleration due to gravity on the moon is 1/6 th of the acceleration
Its unit of measurement is m/s 2. The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body is known as acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol 'g'. G = gm/r² and is about 3.71 m/s². [1] over the entire surface, the variation in gravitational. The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the.
Acceleration due to gravity on moon is 1/6 of the acceleration due to
This means that on the moon, you can jump higher, throw farther, and carry heavier. The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body is known as acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol 'g'. On mars, it can be calculated using the formula: It is equal to 1.625 m/s 2. Its unit of.
Acceleration due to gravity on moon is 1/6 of the acceleration due to
The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body is known as acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol 'g'. The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is approximately 1.625 m/s 2, about 16.6% that on earth's surface or 0.166 ɡ. On mars, it can be calculated using the formula:.
[ANSWERED] Acceleration due to gravity on moon is 1 of the acceleration
The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.6 m/s². The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body is known as acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol 'g'. This means that on the moon, you can jump higher, throw farther, and carry heavier. G = gm/r² and is about 3.71.
Acceleration due to gravity on the moon is 1/6 th that of the earth
It is equal to 1.625 m/s 2. [1] over the entire surface, the variation in gravitational. The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body is known as acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol 'g'. On mars, it can be calculated using the formula: This means that on the moon, you can jump.
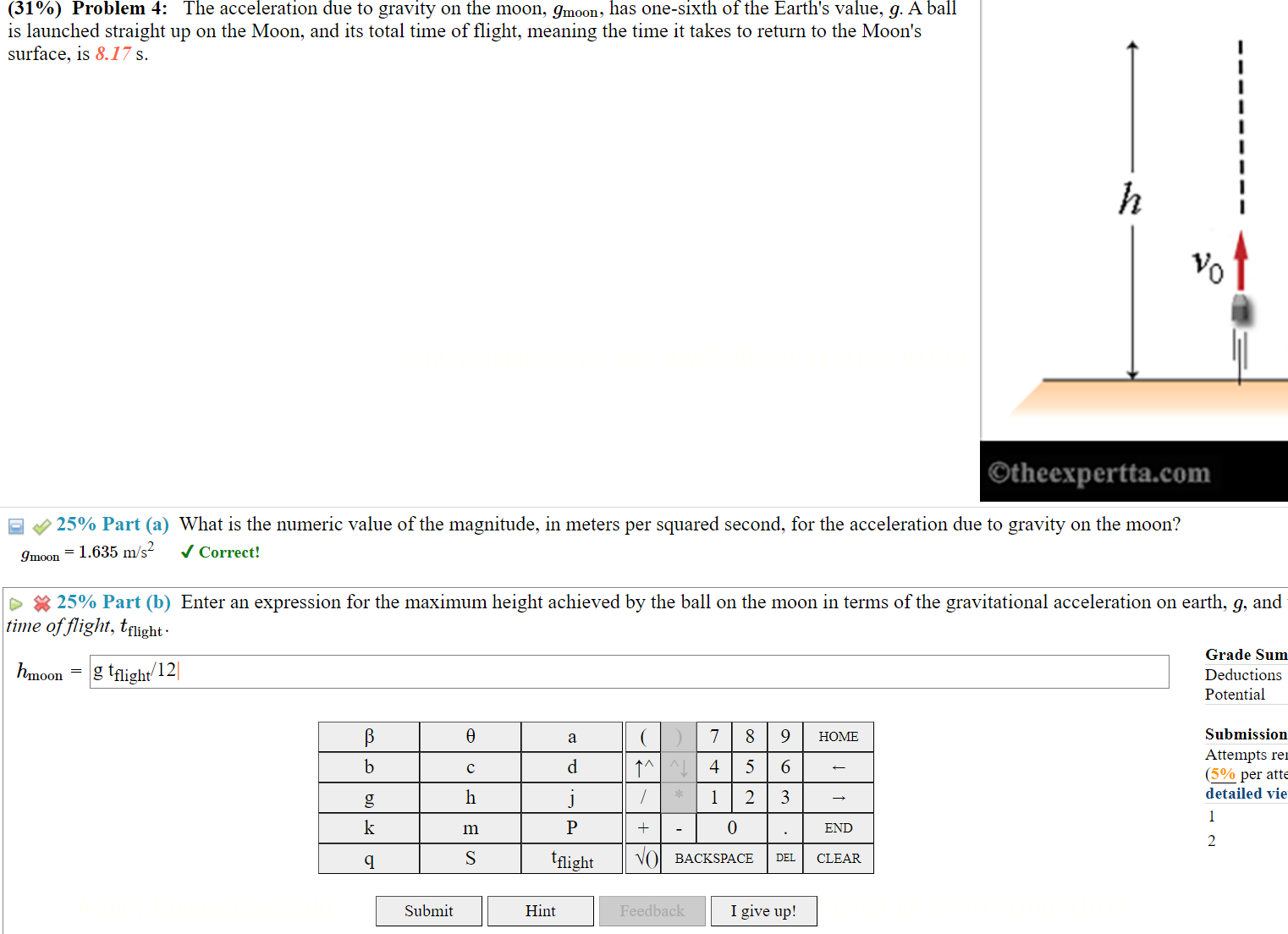
Solved (31\) Problem 4 The acceleration due to gravity on
This means that on the moon, you can jump higher, throw farther, and carry heavier. Its unit of measurement is m/s 2. [1] over the entire surface, the variation in gravitational. It is equal to 1.625 m/s 2. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.6 m/s².
Acceleration due to gravity on the moon is 1/6th of the acceleration
The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.6 m/s². The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is approximately 1.625 m/s 2, about 16.6% that on earth's surface or 0.166 ɡ. On mars, it can be calculated using the formula: The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body.
Acceleration Due To Gravity Calculator Clearance
The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body is known as acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol 'g'. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.6 m/s². On mars, it can be calculated using the formula: The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is approximately.
Acceleration due to gravity on moon is 1/6 of the acceleration due to
This means that on the moon, you can jump higher, throw farther, and carry heavier. On mars, it can be calculated using the formula: The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is approximately 1.625 m/s 2, about 16.6% that on earth's surface or 0.166 ɡ. G = gm/r² and is about 3.71 m/s². [1] over the.
On the moon's surface the acceleration due to gravity is 1.67 { ms
On mars, it can be calculated using the formula: The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body is known as acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol 'g'. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.6 m/s². [1] over the entire surface, the variation in gravitational. The acceleration due to.
The Acceleration Due To Gravity On The Moon Is About 1.6 M/S².
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is approximately 1.625 m/s 2, about 16.6% that on earth's surface or 0.166 ɡ. This means that on the moon, you can jump higher, throw farther, and carry heavier. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is about 1.62 m/s^2, while on earth, it’s around 9.81 m/s^2. It is equal to 1.625 m/s 2.
On Mars, It Can Be Calculated Using The Formula:
Its unit of measurement is m/s 2. G = gm/r² and is about 3.71 m/s². [1] over the entire surface, the variation in gravitational. The force that pulls a freely falling object towards the mass of a body is known as acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol 'g'.



![[ANSWERED] Acceleration due to gravity on moon is 1 of the acceleration](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20210403023715267524-3003478.jpg?h=512)