What Is Covalent Character
What Is Covalent Character - The ionic bond can have a covalent character whenever the cation draws the electron cloud of the anion, causing polarisation and the electron clouds to expand out towards the cation that is. We discussed what is covalent character significance in ionic bonds. If the electrons are pulled away from the negatively charged ion enough, the electrons are held ‘between’ the ions; For example, the ionic compound licl 2 sh ows. Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal) ion is highly charge dense and can polarise the counter ion causing electrons to be shared between the two ions rather than. Ionic compounds generally show partial covalent character.
For example, the ionic compound licl 2 sh ows. The ionic bond can have a covalent character whenever the cation draws the electron cloud of the anion, causing polarisation and the electron clouds to expand out towards the cation that is. Ionic compounds generally show partial covalent character. We discussed what is covalent character significance in ionic bonds. Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal) ion is highly charge dense and can polarise the counter ion causing electrons to be shared between the two ions rather than. If the electrons are pulled away from the negatively charged ion enough, the electrons are held ‘between’ the ions;
Ionic compounds generally show partial covalent character. We discussed what is covalent character significance in ionic bonds. If the electrons are pulled away from the negatively charged ion enough, the electrons are held ‘between’ the ions; Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal) ion is highly charge dense and can polarise the counter ion causing electrons to be shared between the two ions rather than. The ionic bond can have a covalent character whenever the cation draws the electron cloud of the anion, causing polarisation and the electron clouds to expand out towards the cation that is. For example, the ionic compound licl 2 sh ows.
Covalent Bond Definition, Examples, Types, Properties, & FAQs
We discussed what is covalent character significance in ionic bonds. Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal) ion is highly charge dense and can polarise the counter ion causing electrons to be shared between the two ions rather than. The ionic bond can have a covalent character whenever the cation draws the electron cloud of the.
The compound possessing maximum covalent character among the following is..
The ionic bond can have a covalent character whenever the cation draws the electron cloud of the anion, causing polarisation and the electron clouds to expand out towards the cation that is. For example, the ionic compound licl 2 sh ows. We discussed what is covalent character significance in ionic bonds. Ionic compounds generally show partial covalent character. If the.
Covalent and Ionic Character (ALevel) ChemistryStudent
Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal) ion is highly charge dense and can polarise the counter ion causing electrons to be shared between the two ions rather than. If the electrons are pulled away from the negatively charged ion enough, the electrons are held ‘between’ the ions; For example, the ionic compound licl 2 sh.
Covalent Bond Biology Simple
We discussed what is covalent character significance in ionic bonds. If the electrons are pulled away from the negatively charged ion enough, the electrons are held ‘between’ the ions; Ionic compounds generally show partial covalent character. Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal) ion is highly charge dense and can polarise the counter ion causing electrons.
How to tell if Ionic Bond or Covalent Bond Worksheets Library
We discussed what is covalent character significance in ionic bonds. Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal) ion is highly charge dense and can polarise the counter ion causing electrons to be shared between the two ions rather than. For example, the ionic compound licl 2 sh ows. If the electrons are pulled away from the.
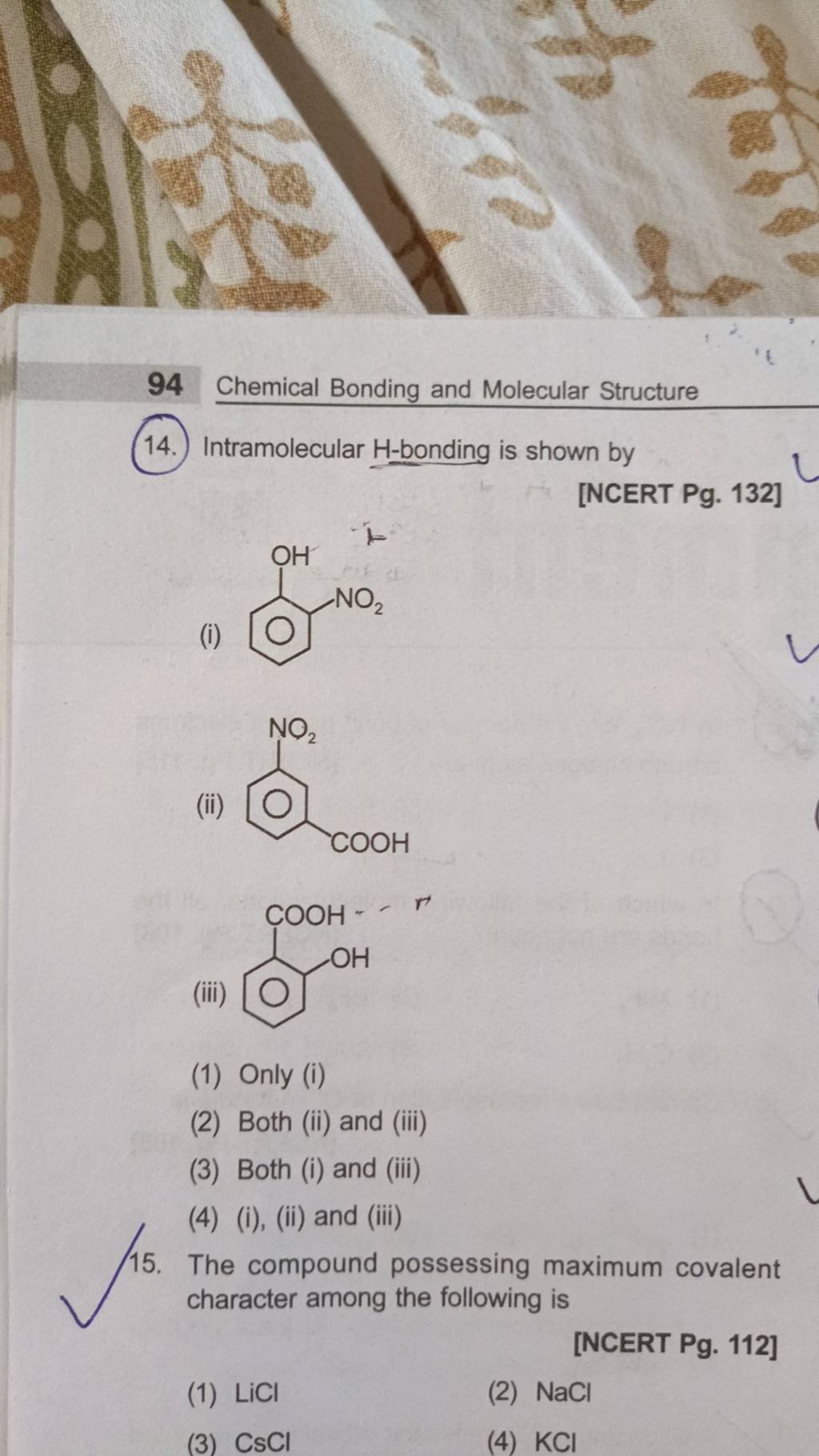
Covalent bond Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
The ionic bond can have a covalent character whenever the cation draws the electron cloud of the anion, causing polarisation and the electron clouds to expand out towards the cation that is. For example, the ionic compound licl 2 sh ows. Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal) ion is highly charge dense and can polarise.
Covalent Bonding Questions and Revision MME Worksheets Library
The ionic bond can have a covalent character whenever the cation draws the electron cloud of the anion, causing polarisation and the electron clouds to expand out towards the cation that is. Ionic compounds generally show partial covalent character. We discussed what is covalent character significance in ionic bonds. Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal).
Covalent Bonding (Biology) — Definition & Role Expii
For example, the ionic compound licl 2 sh ows. If the electrons are pulled away from the negatively charged ion enough, the electrons are held ‘between’ the ions; Ionic compounds generally show partial covalent character. Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal) ion is highly charge dense and can polarise the counter ion causing electrons to.
Ionic vs Covalent Which is which and how to tell them apart
For example, the ionic compound licl 2 sh ows. The ionic bond can have a covalent character whenever the cation draws the electron cloud of the anion, causing polarisation and the electron clouds to expand out towards the cation that is. We discussed what is covalent character significance in ionic bonds. Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive.
Covalent and Ionic Character (ALevel) ChemistryStudent
Ionic compounds generally show partial covalent character. We discussed what is covalent character significance in ionic bonds. The ionic bond can have a covalent character whenever the cation draws the electron cloud of the anion, causing polarisation and the electron clouds to expand out towards the cation that is. Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal).
Ionic Compounds Generally Show Partial Covalent Character.
We discussed what is covalent character significance in ionic bonds. Covalent character occurs in ionic bonds when the postive (usually metal) ion is highly charge dense and can polarise the counter ion causing electrons to be shared between the two ions rather than. The ionic bond can have a covalent character whenever the cation draws the electron cloud of the anion, causing polarisation and the electron clouds to expand out towards the cation that is. If the electrons are pulled away from the negatively charged ion enough, the electrons are held ‘between’ the ions;