What Is The Bond Order For No2
What Is The Bond Order For No2 - If you mean #no^(2+)# , the mo diagram of #no# is: Thus, #no^(2+)# loses the #2b_1# antibonding. Bond order can be determined without the use of mot by counting the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. Its bond order is #2#. In terms of resonance, bond order can be calculated by. The bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. Bond order is characterised as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons in molecular.
Bond order can be determined without the use of mot by counting the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. Thus, #no^(2+)# loses the #2b_1# antibonding. The bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. If you mean #no^(2+)# , the mo diagram of #no# is: Bond order is characterised as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons in molecular. Its bond order is #2#. In terms of resonance, bond order can be calculated by.
If you mean #no^(2+)# , the mo diagram of #no# is: In terms of resonance, bond order can be calculated by. Bond order can be determined without the use of mot by counting the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. Bond order is characterised as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons in molecular. The bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. Thus, #no^(2+)# loses the #2b_1# antibonding. Its bond order is #2#.
Order of bond angle among NO2 ,NO2+ ,NO2− is Filo
The bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. In terms of resonance, bond order can be calculated by. Bond order can be determined without the use of mot by counting the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. Its bond order is #2#. Thus, #no^(2+)# loses the #2b_1# antibonding.
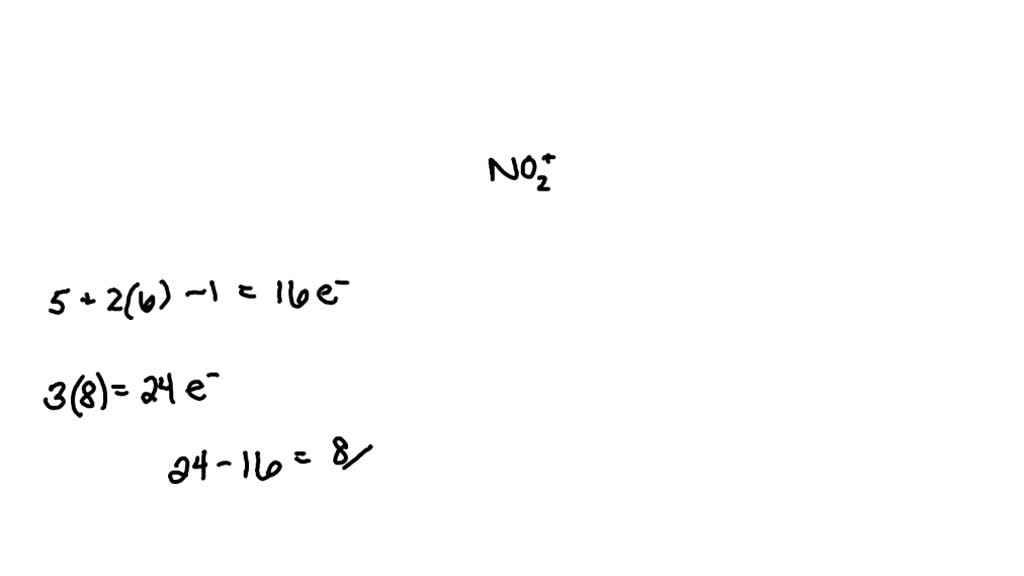
What is the bond order in NO2+?
Bond order is characterised as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons in molecular. Thus, #no^(2+)# loses the #2b_1# antibonding. Its bond order is #2#. The bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. If you mean #no^(2+)# , the mo diagram of #no# is:
The correct order for N O bond length in the given species isI. NO
Thus, #no^(2+)# loses the #2b_1# antibonding. Bond order can be determined without the use of mot by counting the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. Its bond order is #2#. If you mean #no^(2+)# , the mo diagram of #no# is: The bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms.
How To Calculate Bond Order
If you mean #no^(2+)# , the mo diagram of #no# is: Bond order is characterised as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons in molecular. In terms of resonance, bond order can be calculated by. Bond order can be determined without the use of mot by counting the number of bonding and.
Solved The NO bond order in [NO2]−is best described as 1 121
The bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. If you mean #no^(2+)# , the mo diagram of #no# is: Bond order can be determined without the use of mot by counting the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. In terms of resonance, bond order can be calculated by. Its bond order is.
How to find Bond Order of (NO2)+ Chemistry 13524081
The bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. Thus, #no^(2+)# loses the #2b_1# antibonding. Bond order is characterised as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons in molecular. If you mean #no^(2+)# , the mo diagram of #no# is: Bond order can be determined.
SOLVED calculate the bond order for NO2+ ion, regarding all the
Bond order can be determined without the use of mot by counting the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. Thus, #no^(2+)# loses the #2b_1# antibonding. Its bond order is #2#. In terms of resonance, bond order can be calculated by. Bond order is characterised as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons.
26. The correct decreasing order of bond angles of NO2− ,NO2+ and NO2 is..
Bond order is characterised as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons in molecular. Thus, #no^(2+)# loses the #2b_1# antibonding. Bond order can be determined without the use of mot by counting the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. In terms of resonance, bond order can be calculated by. Its bond order.
[Solved] Which one has a higher bond order, NO2 or NO3 ? Show your
Its bond order is #2#. If you mean #no^(2+)# , the mo diagram of #no# is: In terms of resonance, bond order can be calculated by. The bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. Bond order is characterised as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of.
Among NO2 ,NO2+,NO3 , what is the order of bond length and bond angle
The bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. Bond order is characterised as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons in molecular. Bond order can be determined without the use of mot by counting the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. If you mean.
If You Mean #No^(2+)# , The Mo Diagram Of #No# Is:
Bond order can be determined without the use of mot by counting the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. In terms of resonance, bond order can be calculated by. The bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. Its bond order is #2#.
Thus, #No^(2+)# Loses The #2B_1# Antibonding.
Bond order is characterised as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons in molecular.




![Solved The NO bond order in [NO2]−is best described as 1 121](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/2d4/2d47a7dd-9309-4816-ab40-22e1add0f061/php53XYm4)