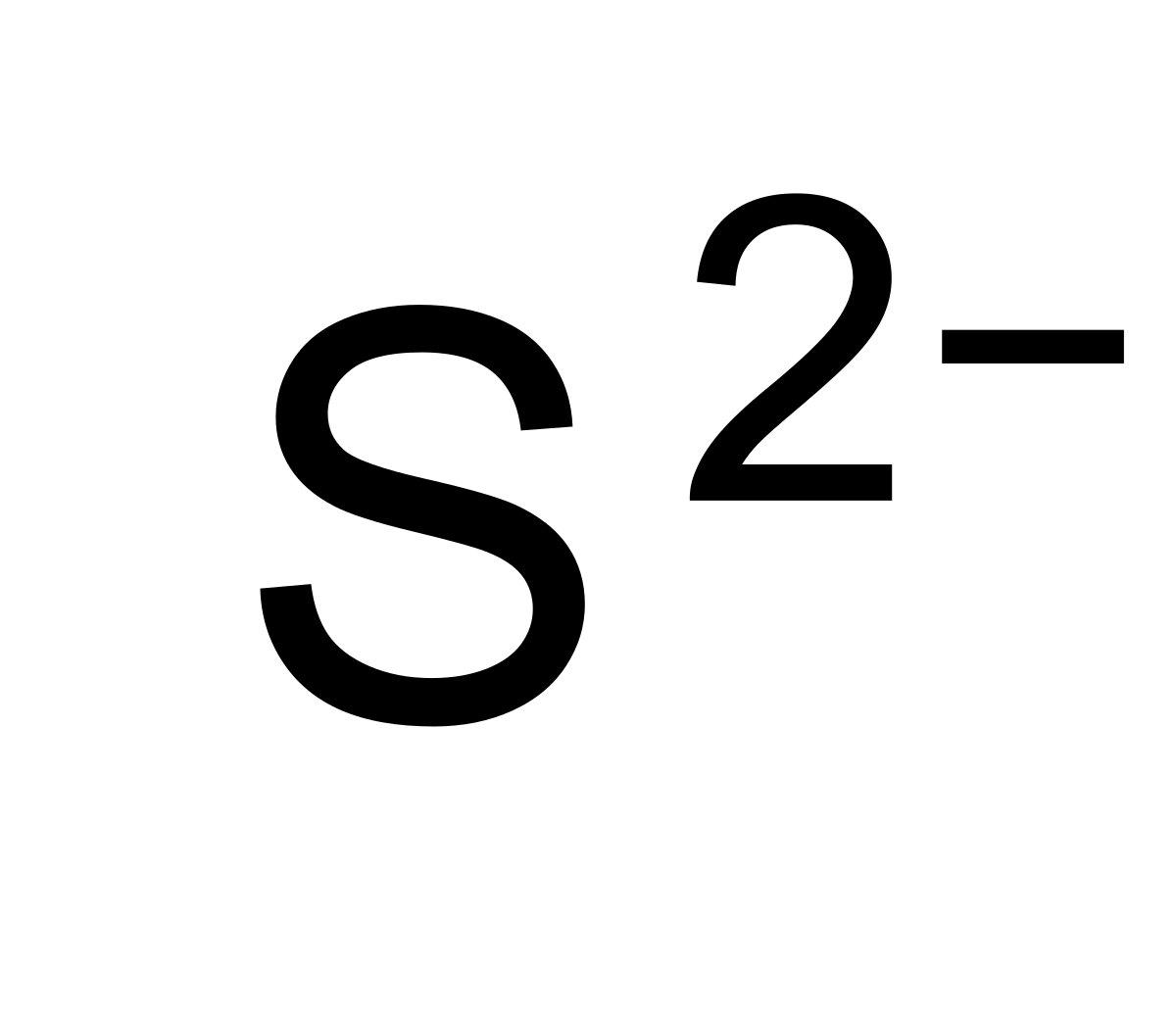What Is The Charge Of Sulfide
What Is The Charge Of Sulfide - Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge; In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons.
Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons. For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge;
Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge; In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons.
Sulfide charge jordoutdoor
For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge; In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons. Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion.
We can draw three inequivalent Lewis structures for carbonyl sulfide
Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge; In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons.
Chargedischarge profiles of bismuth sulfide recorded at 2 A g −1 (a
In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons. For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge; Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion.
Insights into interfacial physiochemistry in sulfide solidstate
In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons. Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge;
Sulfide Wikipedia
Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge; In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons.
SOLVEDFor each of the following ions, write the full electron
Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons. For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge;
Sulfate définition illustrée et explications
For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge; Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons.
Schematic illustration of the different types of interphases between
Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons. For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge;
Sulfide charge atilagrid
In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons. Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge;
How to Write the Formula for Sulfide ion YouTube
For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge; Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. In your case, the sulfide anion, s2−, carries a (2 −) negative charge, which can only mean that it gained electrons.
In Your Case, The Sulfide Anion, S2−, Carries A (2 −) Negative Charge, Which Can Only Mean That It Gained Electrons.
Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. For example, iron( ii ) has a 2+ charge;