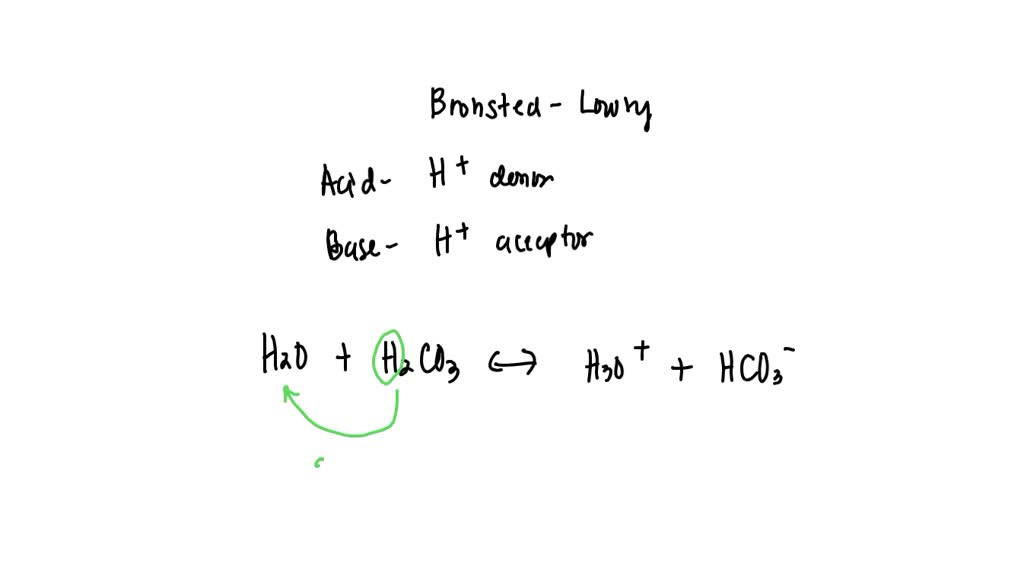What Is The Conjugate Acid Of Hco3
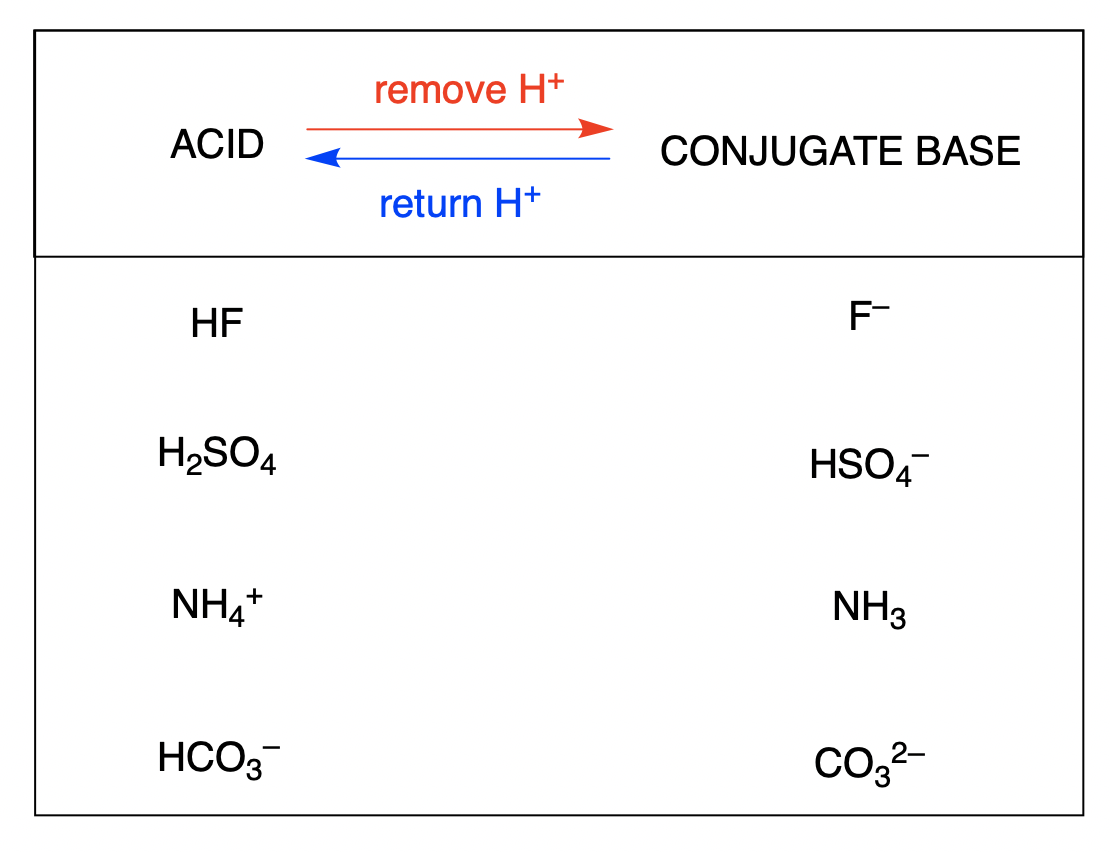
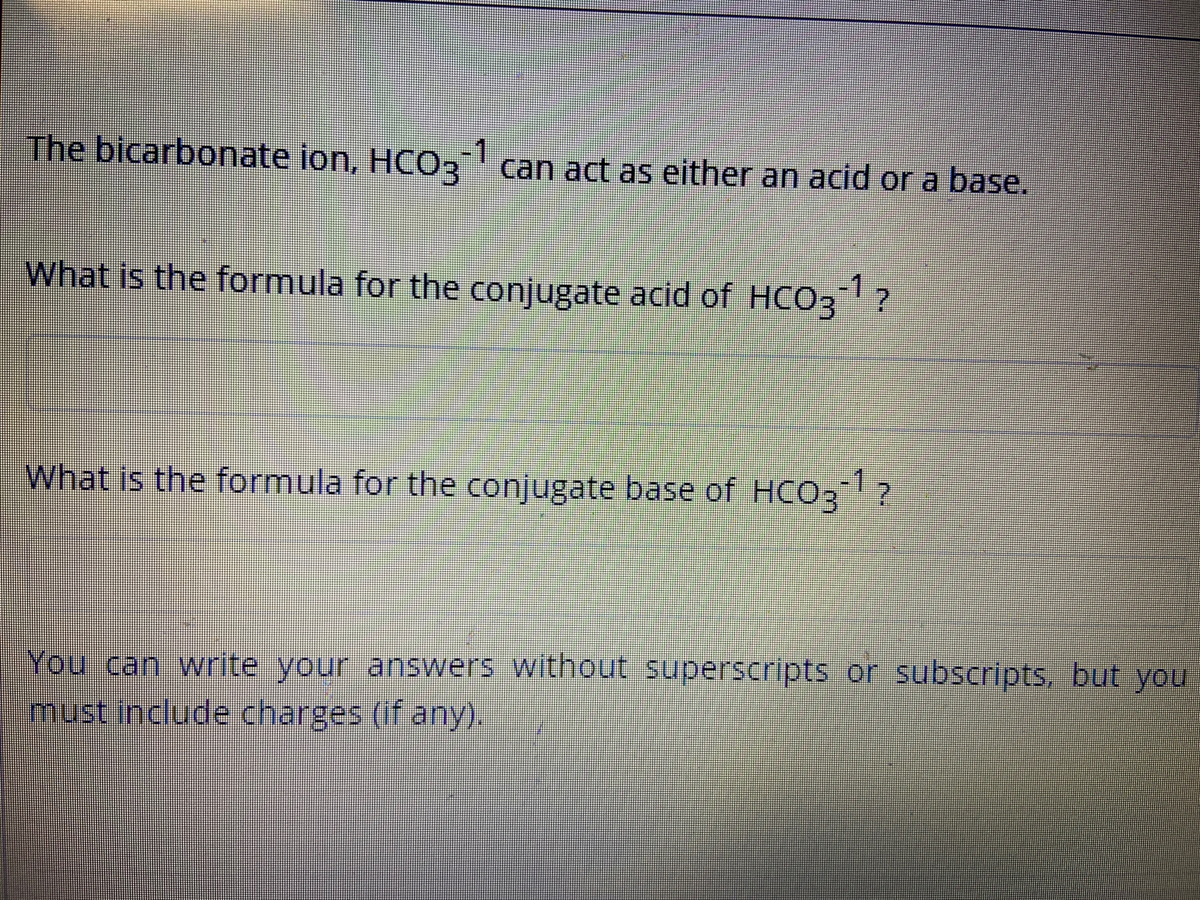
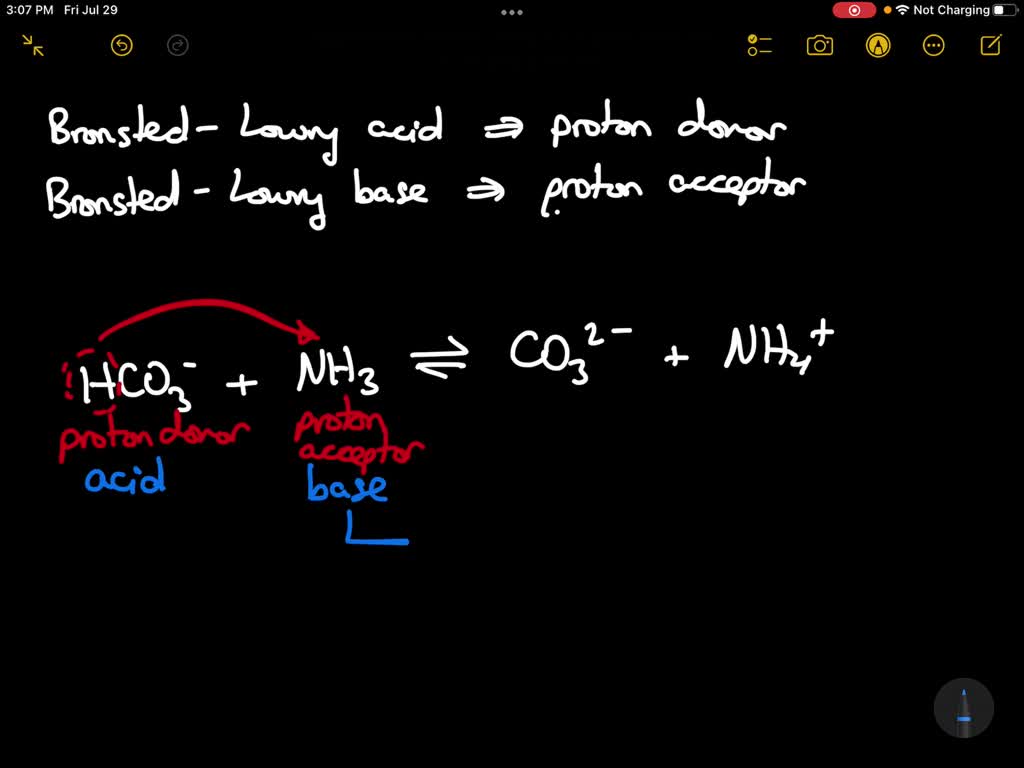
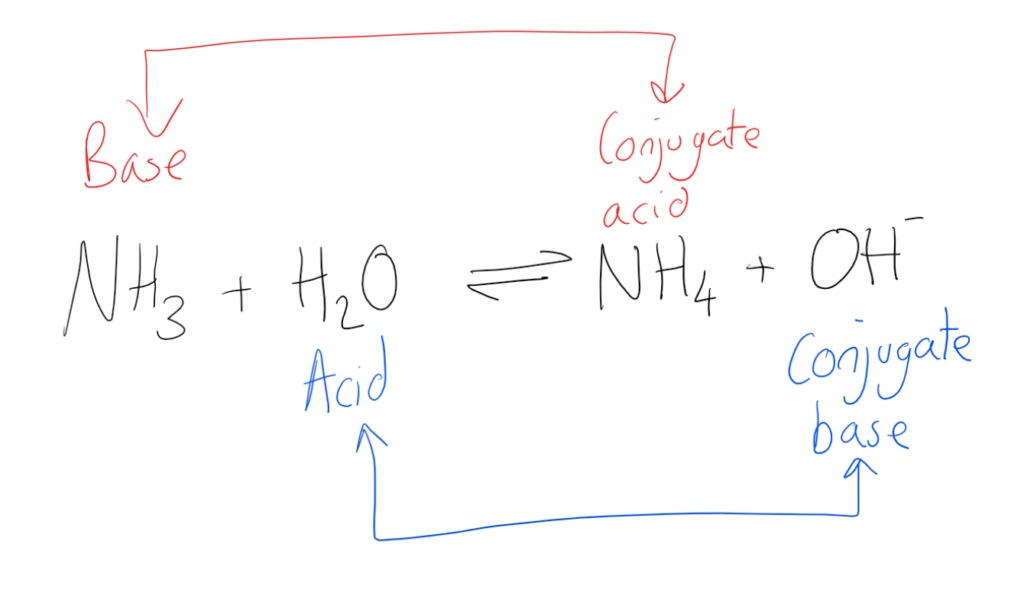
What Is The Conjugate Acid Of Hco3 - This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion. When a proton is added to a base, a conjugate acid is formed. Simply add one proton to the formula of the substance to determine the. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it.
Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion. Simply add one proton to the formula of the substance to determine the. This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. When a proton is added to a base, a conjugate acid is formed.
Simply add one proton to the formula of the substance to determine the. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. When a proton is added to a base, a conjugate acid is formed. This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion.
Answered Identify the conjugate acid for each… bartleby
This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. When a proton is added to a base, a conjugate acid is formed. Simply add one proton to the formula of the substance to determine the. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by.
SOLVED In the following reaction, what is the acid, the base, the conjugate acid, the conjugate
The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. Simply add one proton to the formula of the substance to determine the. When a proton is added to a base, a conjugate acid is formed. This is formed.
How To Draw A Conjugate Acid
When a proton is added to a base, a conjugate acid is formed. This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. Simply add one proton to the.
Solved Exercises What Is The Conjugate Acid Of HCO3?, 47 OFF
When a proton is added to a base, a conjugate acid is formed. Simply add one proton to the formula of the substance to determine the. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by.
Conjugate AcidBase Pairs — Overview & Examples Expii
The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion. This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. When a proton is added to a base, a conjugate acid is formed. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. Simply add one proton to the.
Conjugate acid and conjugate base of HCO3− respectively are Filo
The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion. When a proton is added to a base, a conjugate acid is formed. This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. Simply add one proton to the formula of the substance to determine the. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared.
SOLVED Identify acidbase conjugate pairs. Close Problem (a) What is the conjugate acid of F
When a proton is added to a base, a conjugate acid is formed. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion. Simply add one proton to the.
Conjugate Acids And Bases Acid Base Equilibria
Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion. Simply add one proton to the formula of the substance to determine the. When a proton is added to.
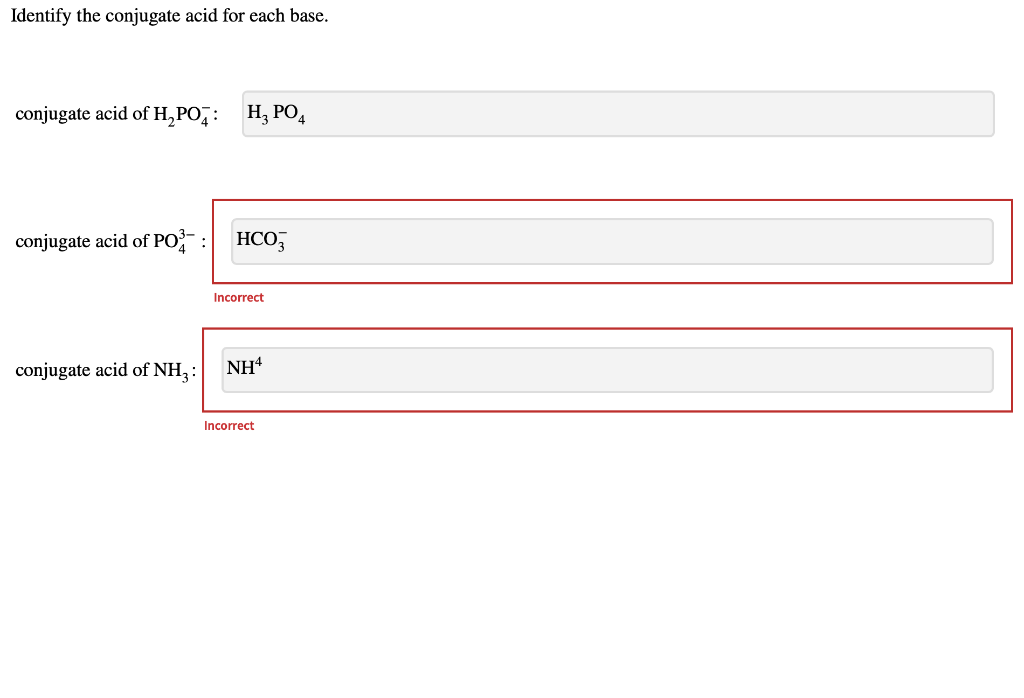
Solved Identify the conjugate acid for each base. conjugate
The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion. Simply add one proton to the formula of the substance to determine the. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. When a proton is added to.
SOLVED For the reaction below, identify the acid, the base, the conjugate acid, and the
This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion. Simply add one proton to the formula of the substance to determine the. When a proton is added to.
Simply Add One Proton To The Formula Of The Substance To Determine The.
The conjugate acid of hco3⁻ (bicarbonate ion) is formed by adding one proton (h⁺) to the ion. When a proton is added to a base, a conjugate acid is formed. Conjugate acids have one extra proton compared to the species that is forming it. This is formed by adding a proton (h+) to the.