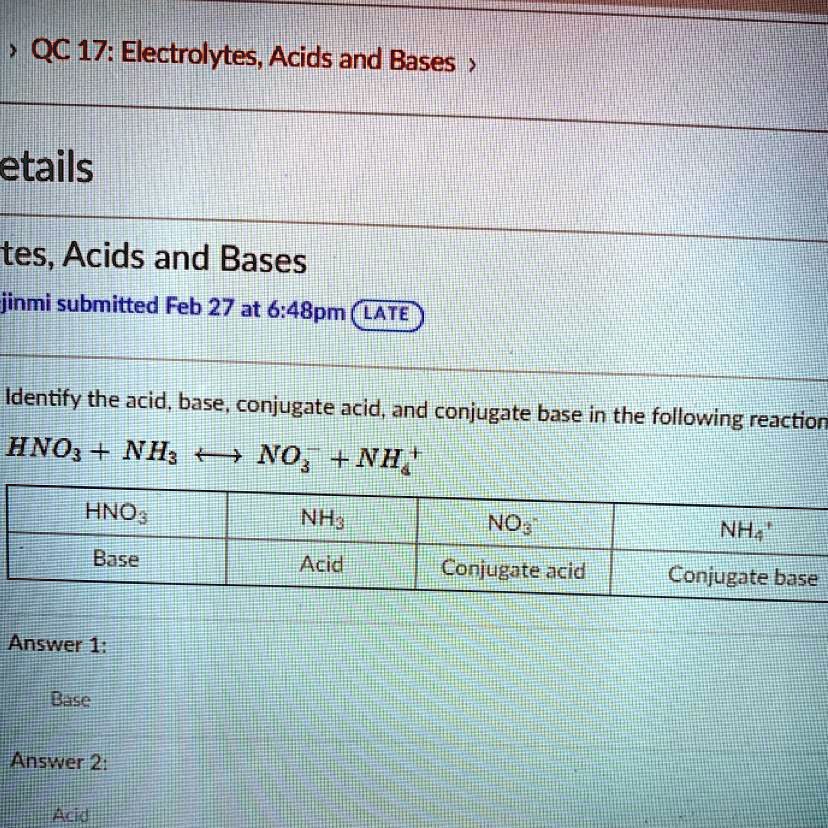
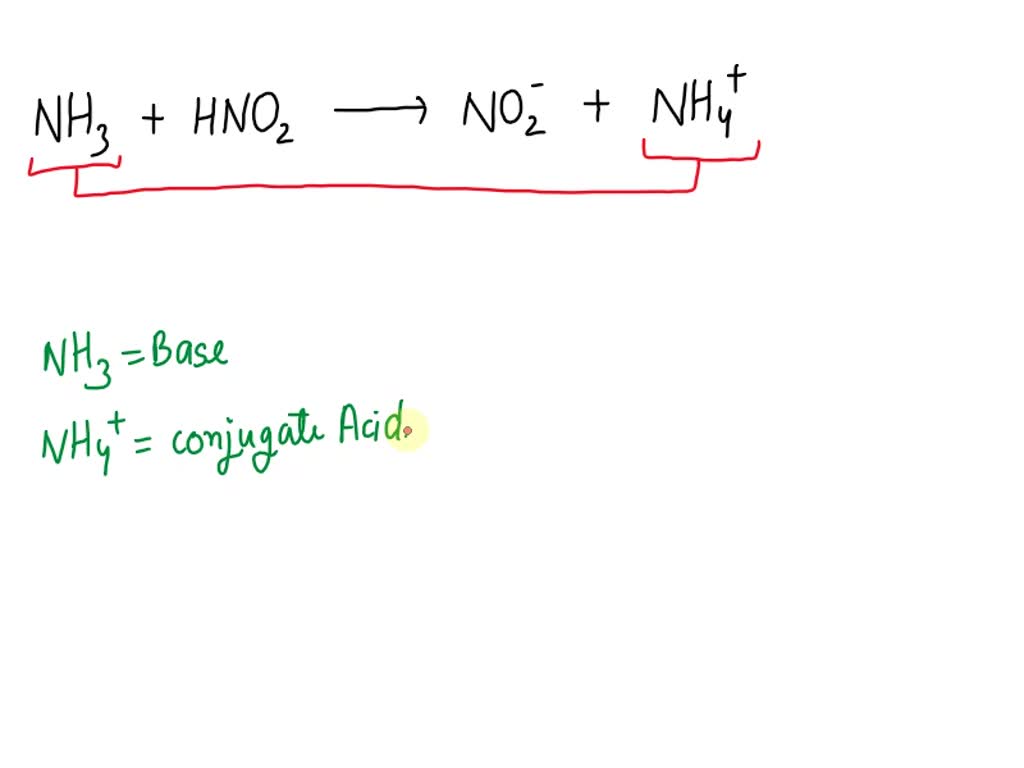
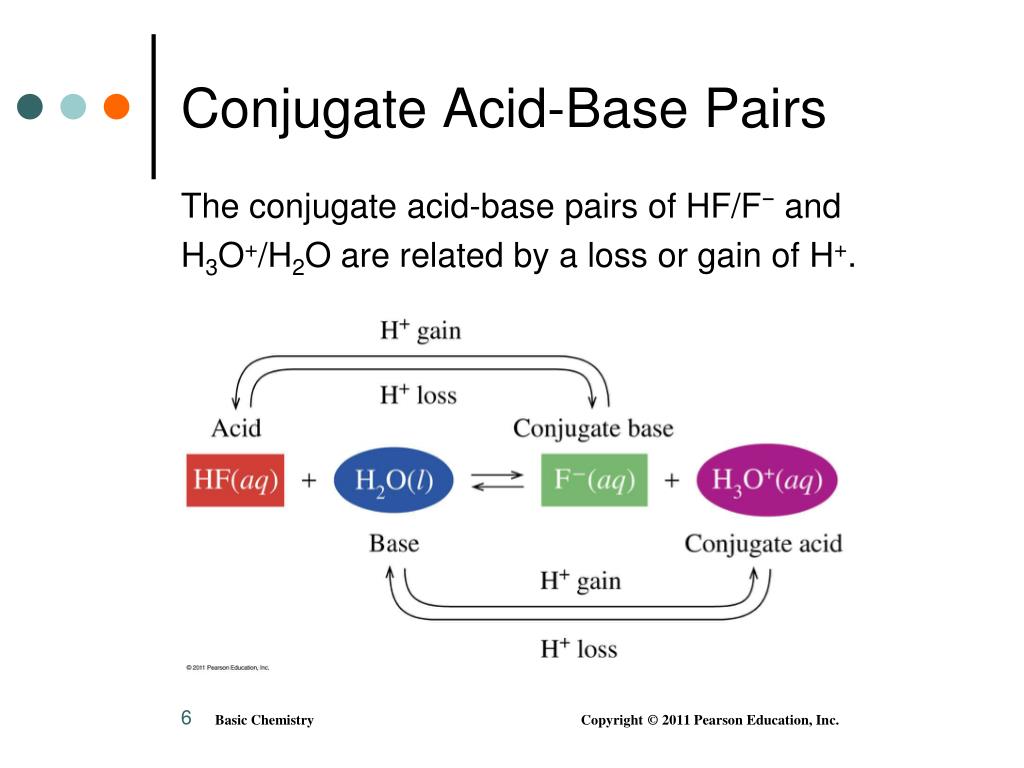
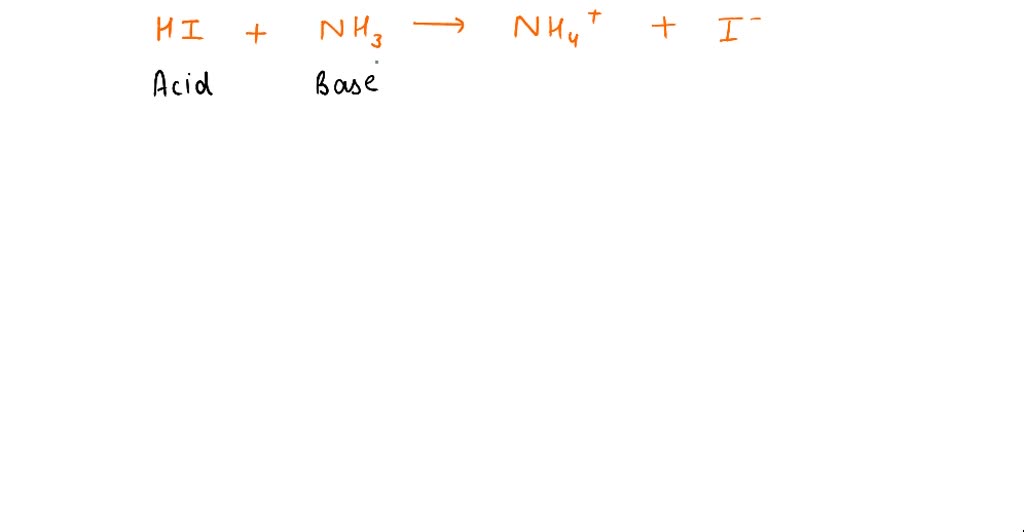What Is The Conjugate Base Of Nh3
What Is The Conjugate Base Of Nh3 - Conjugate base is the compound which is formed when a acid looses a proton i.e a h+ ion. A conjugate base is formed by the removal of a proton (h+) from the parent acid or. When nh3 accepts a proton (h+), it forms nh4+. The conjugate acid of nh3 (ammonia) is nh4+ (ammonium ion). Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. The conjugate base of nh4+ is nh3 (ammonia). This species does not exist in water, but it is the characteristic anion in liquid ammonia, a water like solvent that will support. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. When a proton is removed from an acid, a conjugate.
The conjugate base of nh4+ is nh3 (ammonia). Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. When a proton is removed from an acid, a conjugate. This species does not exist in water, but it is the characteristic anion in liquid ammonia, a water like solvent that will support. The conjugate acid of nh3 (ammonia) is nh4+ (ammonium ion). A conjugate base is formed by the removal of a proton (h+) from the parent acid or. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. Conjugate base is the compound which is formed when a acid looses a proton i.e a h+ ion. When nh3 accepts a proton (h+), it forms nh4+.
This species does not exist in water, but it is the characteristic anion in liquid ammonia, a water like solvent that will support. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. Conjugate base is the compound which is formed when a acid looses a proton i.e a h+ ion. When a proton is removed from an acid, a conjugate. The conjugate base of nh4+ is nh3 (ammonia). A conjugate base is formed by the removal of a proton (h+) from the parent acid or. The conjugate acid of nh3 (ammonia) is nh4+ (ammonium ion). When nh3 accepts a proton (h+), it forms nh4+.
Conjugate Acid Base Chart
When a proton is removed from an acid, a conjugate. When nh3 accepts a proton (h+), it forms nh4+. A conjugate base is formed by the removal of a proton (h+) from the parent acid or. Conjugate base is the compound which is formed when a acid looses a proton i.e a h+ ion. The conjugate base of nh4+ is.
SOLVED Question 10 (1 point) Saved In the reaction HzS + NHz" NH3 HS
When nh3 accepts a proton (h+), it forms nh4+. The conjugate base of nh4+ is nh3 (ammonia). Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. The conjugate acid of nh3 (ammonia) is nh4+ (ammonium ion). Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons.
SOLVED Label the acid base conjugate pairs in the following reaction
The conjugate acid of nh3 (ammonia) is nh4+ (ammonium ion). When a proton is removed from an acid, a conjugate. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. The conjugate base of nh4+ is nh3 (ammonia). This species does not exist in water, but it is the characteristic anion in liquid ammonia, a water like solvent that will.
SOLVED'Identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base in
The conjugate base of nh4+ is nh3 (ammonia). When a proton is removed from an acid, a conjugate. When nh3 accepts a proton (h+), it forms nh4+. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons.
Solved Give the conjugate base for each compound below Acid
Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. This species does not exist in water, but it is the characteristic anion in liquid ammonia, a water like solvent that will support. A conjugate base is formed by the removal of a proton (h+) from the parent acid or. When nh3 accepts a proton.
(Get Answer) Identify The Conjugate Acid For Each Base. Conjugate
Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. When a proton is removed from an acid, a conjugate. A conjugate base is formed by the removal of a proton (h+) from the parent acid or. Conjugate base is the compound which is formed when a acid looses a proton i.e a h+ ion. The conjugate acid of nh3.
SOLVED Identify the conjugate acid or base of each of the following
When nh3 accepts a proton (h+), it forms nh4+. A conjugate base is formed by the removal of a proton (h+) from the parent acid or. This species does not exist in water, but it is the characteristic anion in liquid ammonia, a water like solvent that will support. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that.
SOLVED QUESTION 8 Determine the acid, base, conjugate acid conjugate
A conjugate base is formed by the removal of a proton (h+) from the parent acid or. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. When nh3 accepts a proton (h+), it forms nh4+. The conjugate base of nh4+ is nh3 (ammonia). When a proton is removed from an acid, a conjugate.
Conjugate Acid Vs Conjugate Base
Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. Conjugate base is the compound which is formed when a acid looses a proton i.e a h+ ion. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. When a proton is removed from an acid, a conjugate. When nh3 accepts a proton (h+), it.
Answered acid conjugate base base conjugate acid… bartleby
This species does not exist in water, but it is the characteristic anion in liquid ammonia, a water like solvent that will support. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. The conjugate base of nh4+ is nh3 (ammonia). When nh3 accepts a proton (h+), it forms nh4+. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases.
The Conjugate Acid Of Nh3 (Ammonia) Is Nh4+ (Ammonium Ion).
Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. Conjugate base is the compound which is formed when a acid looses a proton i.e a h+ ion. A conjugate base is formed by the removal of a proton (h+) from the parent acid or. The conjugate base of nh4+ is nh3 (ammonia).
This Species Does Not Exist In Water, But It Is The Characteristic Anion In Liquid Ammonia, A Water Like Solvent That Will Support.
When nh3 accepts a proton (h+), it forms nh4+. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. When a proton is removed from an acid, a conjugate.