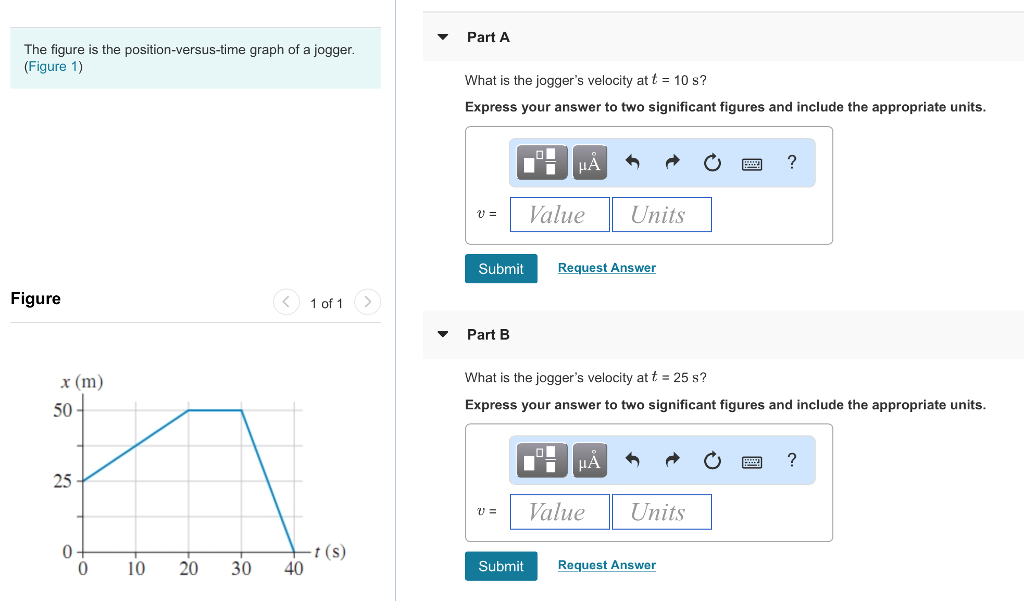
What Is The Jogger S Velocity At T 10 S
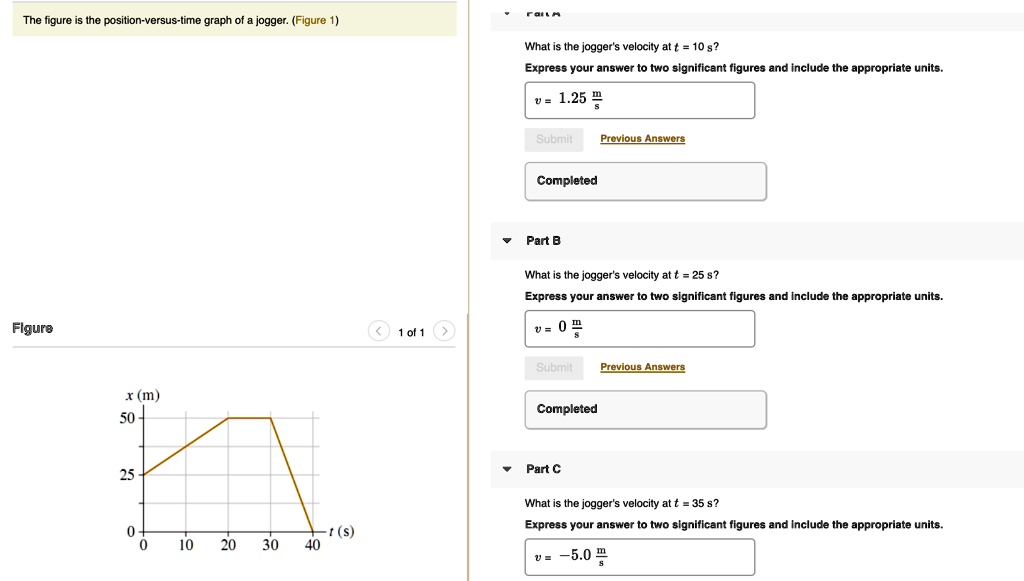
What Is The Jogger S Velocity At T 10 S - We can see from the graph that the. The slope of the position. The figure below is the position vs. (a) what is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s? At t = 2.0 s, what are the particle’s (a) position, (b) velocity, and (c) acceleration? At t = 10 s, we can determine the jogger's velocity by finding the slope of the. Velocity at t = 10 s: Identify two points on the graph around t = 10 s, for example, (t1, x1) and (t2, x2). Use the formula for slope:. At t = 10 s, the jogger's velocity can be calculated by dividing the change in position by the change in time.
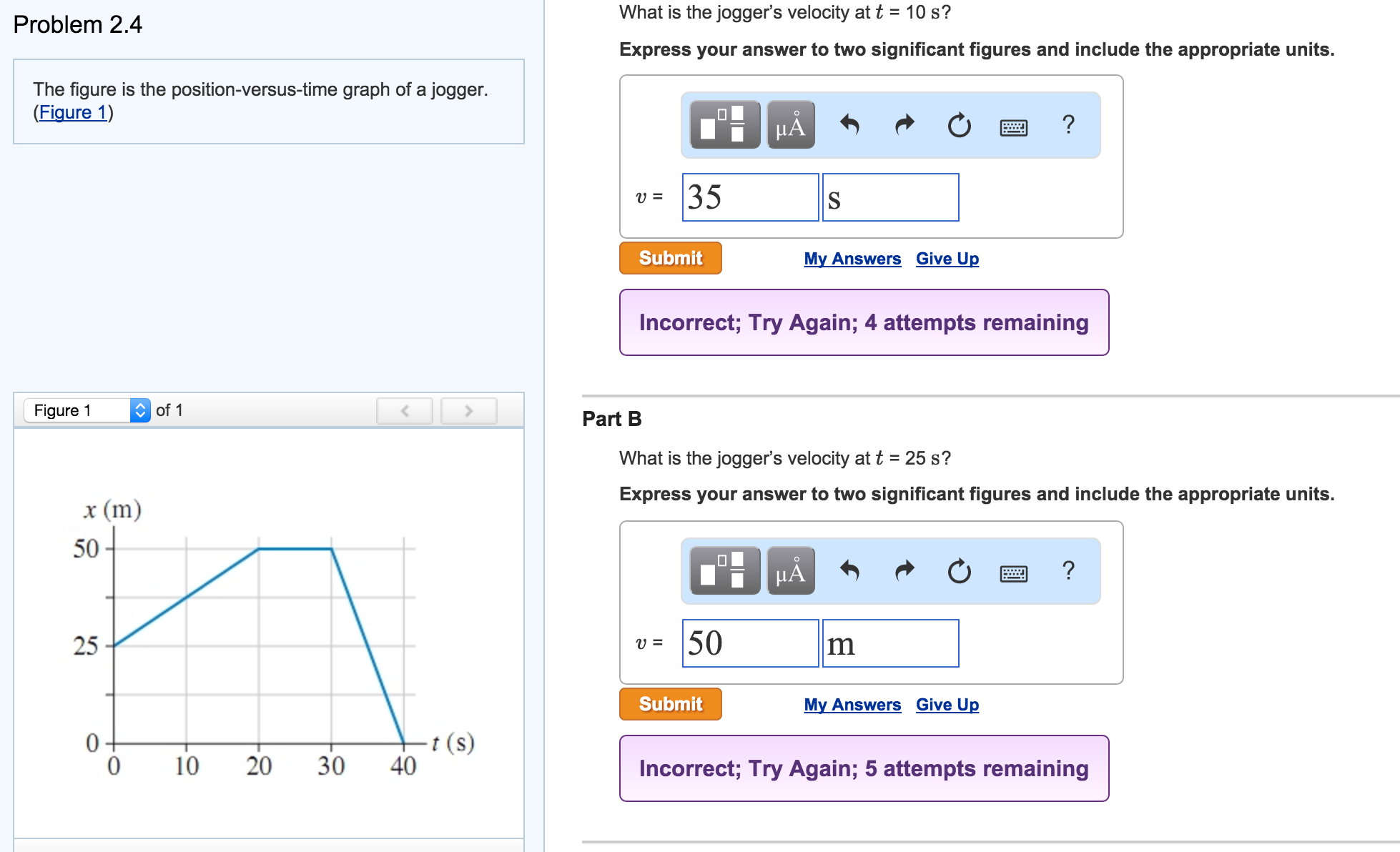
What is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s, at t = 25 s, and at t = 35 s? At t = 10 s, the jogger's velocity can be calculated by dividing the change in position by the change in time. The figure below is the position vs. At t = 10 s, we can determine the jogger's velocity by finding the slope of the. Time graph of a jogger. Use the formula for slope:. Particle c has an initial. The slope of the position. At t = 2.0 s, what are the particle’s (a) position, (b) velocity, and (c) acceleration? What is the jogger’s velocity at a) t = 10s (lc) b) t = 25s (lc) c) t = 35 s (lc) 4
At t = 10 s, the jogger's velocity can be calculated by dividing the change in position by the change in time. The figure below is the position vs. Velocity at t = 10 s: The slope of the position. We can see from the graph that the. Particle c has an initial. What is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s, at t = 25 s, and at t = 35 s? Use the formula for slope:. (a) what is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s? At t = 2.0 s, what are the particle’s (a) position, (b) velocity, and (c) acceleration?
the ligure the position versus time graph of jogger figure 1 what the
The slope of the position. The jogger is a particle. We can see from the graph that the. At t = 2.0 s, what are the particle’s (a) position, (b) velocity, and (c) acceleration? Use the formula for slope:.
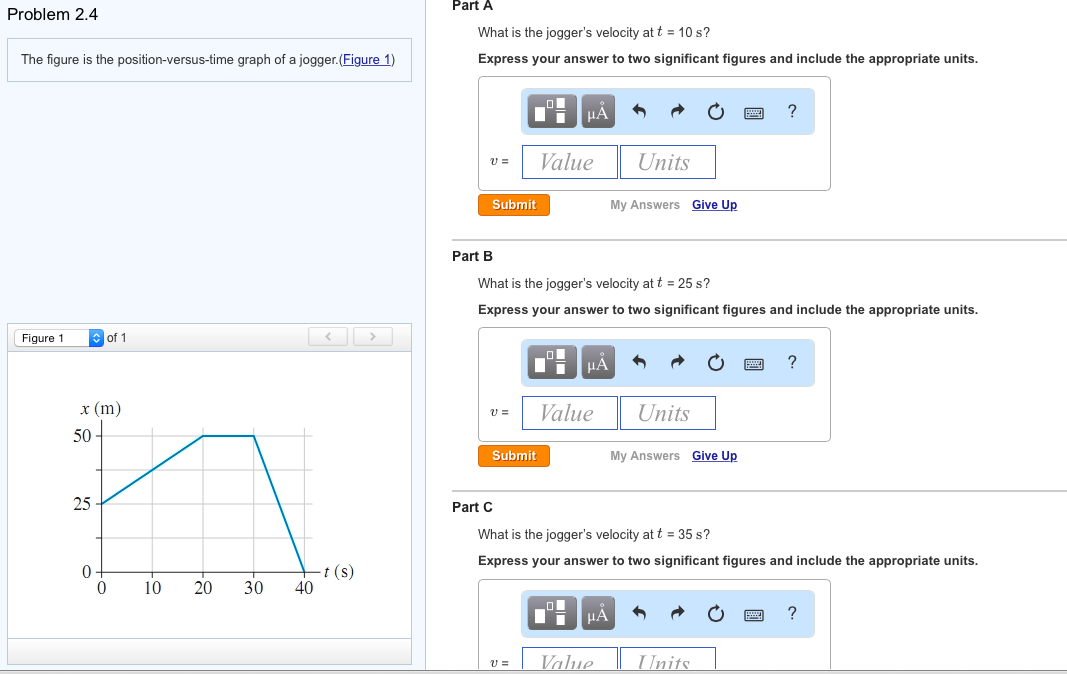
Solved Part C What is the jogger’s velocity at t = 35 s?
Velocity at t = 10 s: (a) what is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s? At t = 10 s, we can determine the jogger's velocity by finding the slope of the. At t = 2.0 s, what are the particle’s (a) position, (b) velocity, and (c) acceleration? We can see from the graph that the.
How To Calculate Average Velocity Haiper
Use the formula for slope:. What is the jogger’s velocity at a) t = 10s (lc) b) t = 25s (lc) c) t = 35 s (lc) 4 At t = 10 s, we can determine the jogger's velocity by finding the slope of the. We can see from the graph that the. Velocity at t = 10 s:
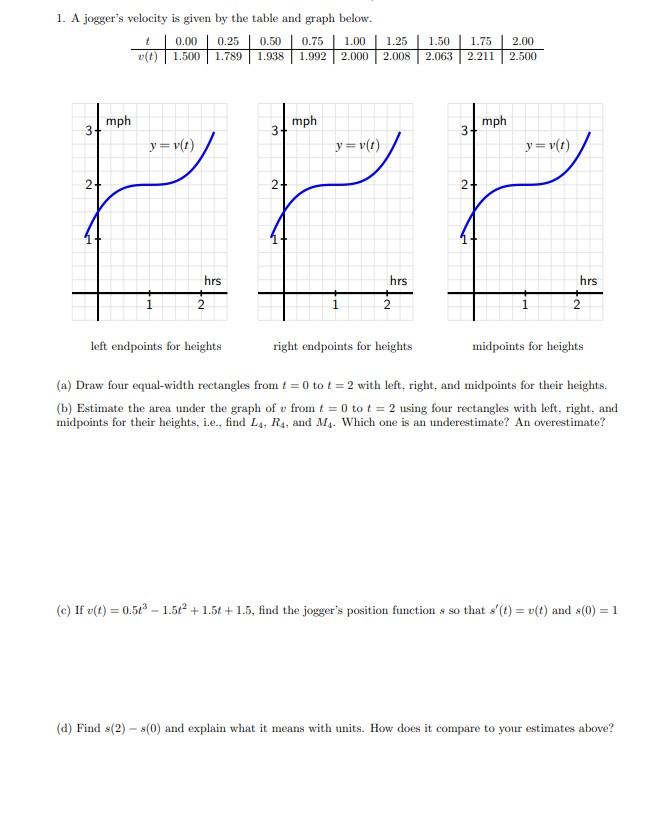
Solved 1. A jogger's velocity is given by the table and
At t = 10 s, the jogger's velocity can be calculated by dividing the change in position by the change in time. Particle c has an initial. (a) what is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s? At t = 10 s, we can determine the jogger's velocity by finding the slope of the. The slope of the position.
Solved Part A The figure is the positionversustime graph
What is the jogger’s velocity at a) t = 10s (lc) b) t = 25s (lc) c) t = 35 s (lc) 4 Time graph of a jogger. At t = 2.0 s, what are the particle’s (a) position, (b) velocity, and (c) acceleration? Use the formula for slope:. Identify two points on the graph around t = 10 s,.
Solved Problem 2.4 The Figure Is The Positionversustime...
What is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s, at t = 25 s, and at t = 35 s? The figure below is the position vs. Time graph of a jogger. What is the jogger’s velocity at a) t = 10s (lc) b) t = 25s (lc) c) t = 35 s (lc) 4 At t = 10.
Solved The position vs time of an jogger is shown in the
At t = 10 s, the jogger's velocity can be calculated by dividing the change in position by the change in time. We can see from the graph that the. At t = 10 s, we can determine the jogger's velocity by finding the slope of the. Identify two points on the graph around t = 10 s, for example,.
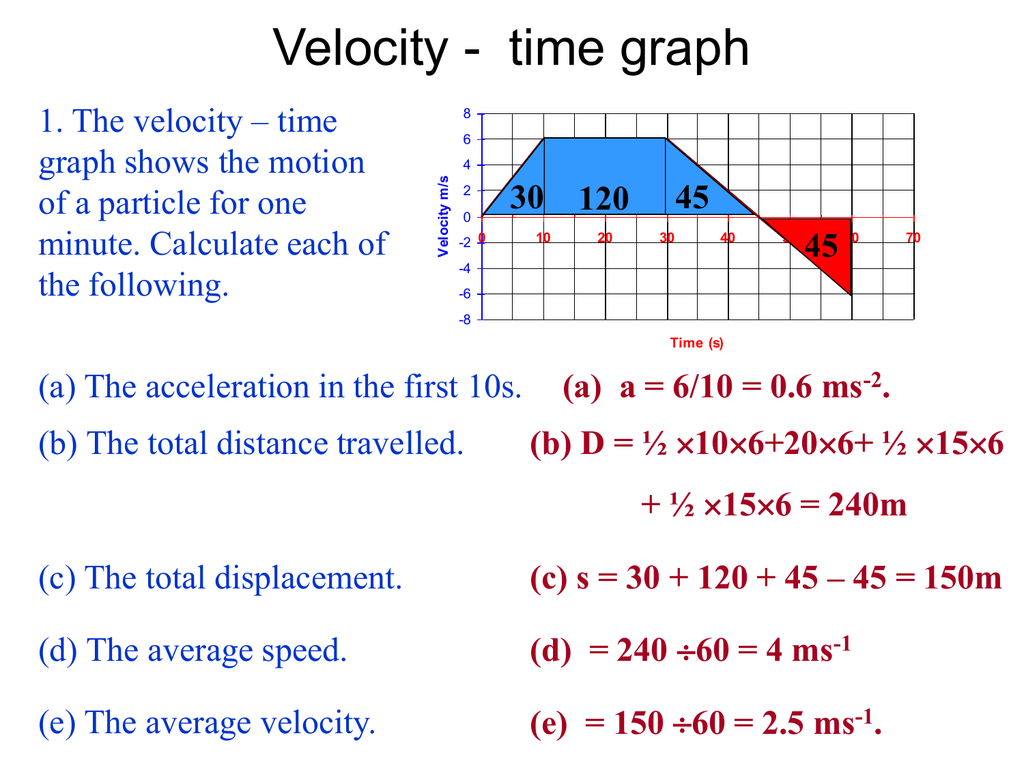
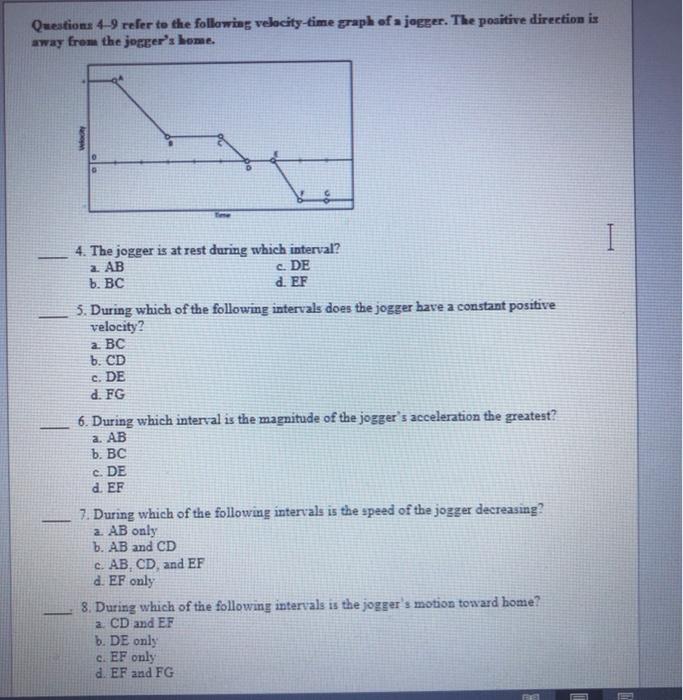
Solved Questions 49 refer to the following velocitytime
The jogger is a particle. Use the formula for slope:. Particle c has an initial. (a) what is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s? We can see from the graph that the.
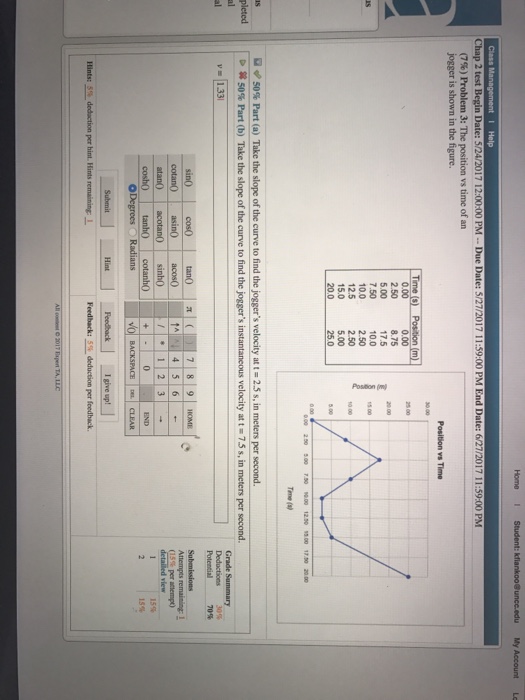
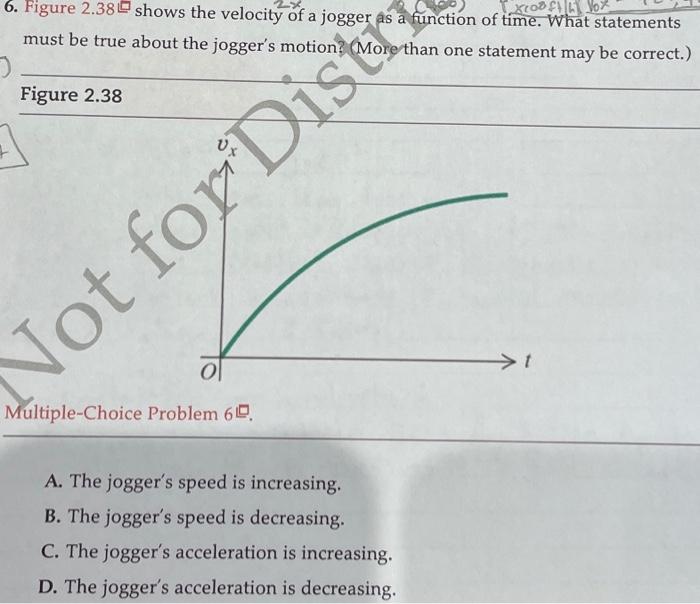
Solved 6. Figure 2.38 shows the velocity of a jogger as a
What is the jogger’s velocity at a) t = 10s (lc) b) t = 25s (lc) c) t = 35 s (lc) 4 What is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s, at t = 25 s, and at t = 35 s? Identify two points on the graph around t = 10 s, for example, (t1, x1) and.
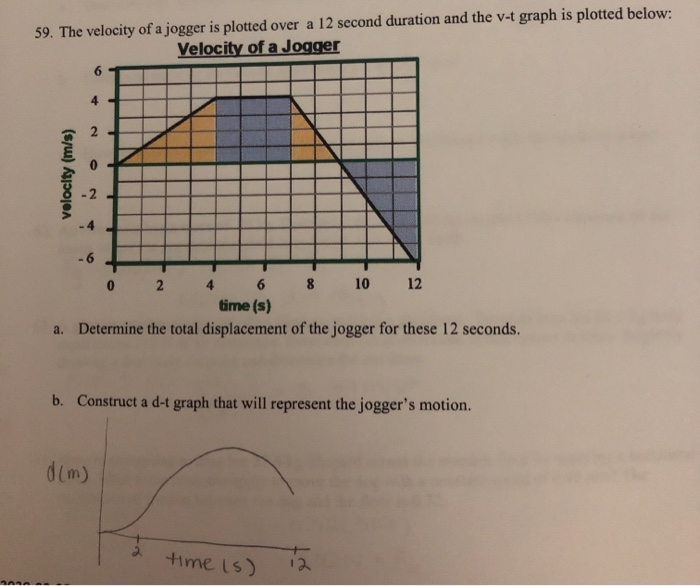
Solved 59. The velocity of a jogger is plotted over a 12
The slope of the position. At t = 10 s, the jogger's velocity can be calculated by dividing the change in position by the change in time. Identify two points on the graph around t = 10 s, for example, (t1, x1) and (t2, x2). (a) what is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s? The jogger is a.
What Is The Jogger’s Velocity At A) T = 10S (Lc) B) T = 25S (Lc) C) T = 35 S (Lc) 4
At t = 10 s, the jogger's velocity can be calculated by dividing the change in position by the change in time. What is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s, at t = 25 s, and at t = 35 s? Particle c has an initial. At t = 2.0 s, what are the particle’s (a) position, (b) velocity, and (c) acceleration?
The Slope Of The Position.
The jogger is a particle. Use the formula for slope:. The figure below is the position vs. At t = 10 s, we can determine the jogger's velocity by finding the slope of the.
Velocity At T = 10 S:
Identify two points on the graph around t = 10 s, for example, (t1, x1) and (t2, x2). (a) what is the jogger’s velocity at t = 10 s? Time graph of a jogger. We can see from the graph that the.